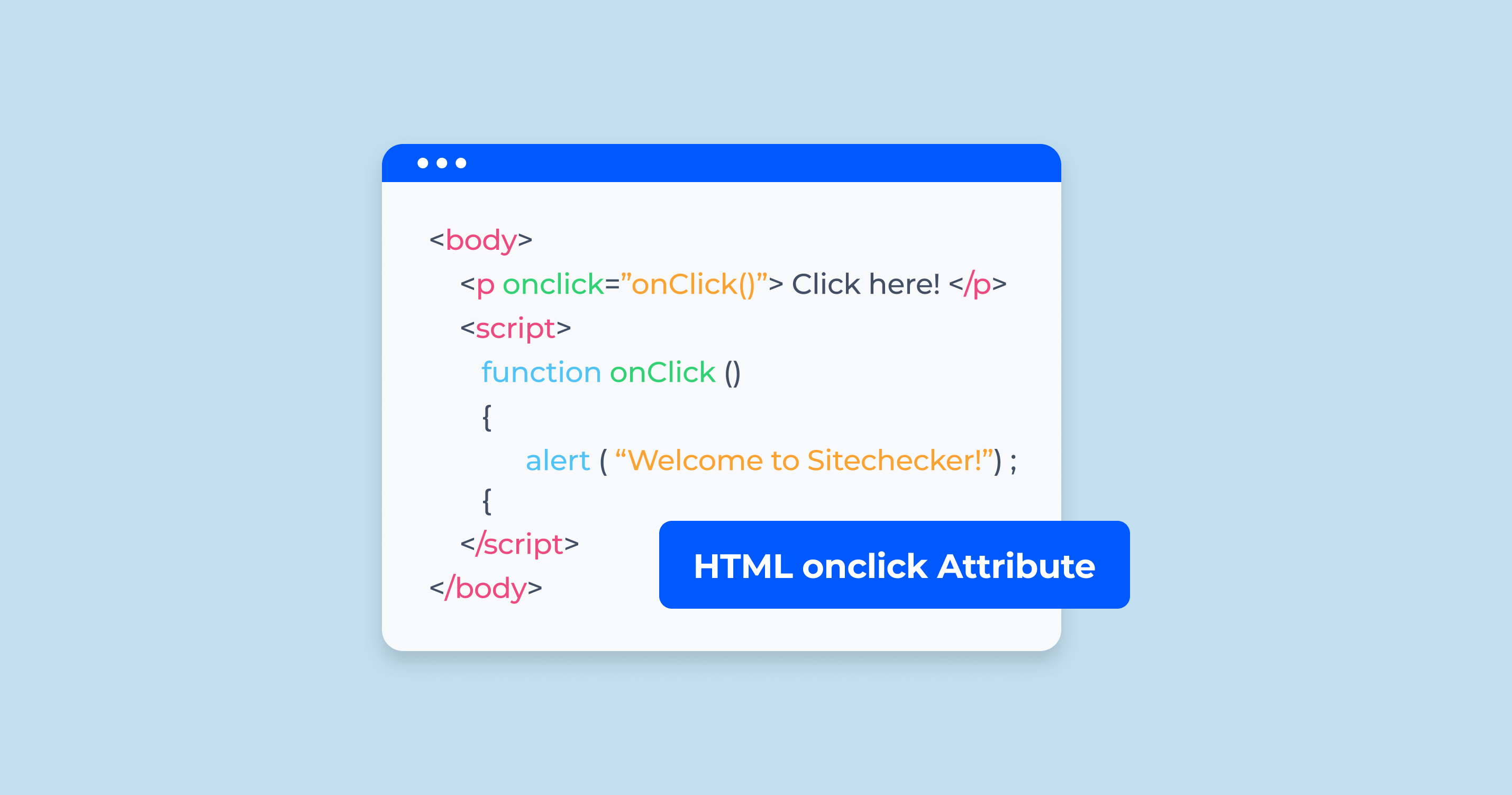
What is HTML Onclick Attribute?
The HTML onclick attribute is an event attribute that is used to specify a JavaScript function to be executed when a user clicks on an HTML element. It can be used on any HTML element, but it is most commonly used on buttons.
How to Use HTML onclick Attribute?
To use the onclick attribute, simply add it to the opening tag of the HTML element that you want to be clickable and specify the name of the JavaScript function that you want to be executed:
Syntax
<tagname onclick="script"></tagname>Example using on click to display an alert message:
<button onclick="alert('Hello!')">Click me</button>When you click the button, it will display an alert box with the message “Hello!”.
Using HTML button to call a JavaScript function:
<script>
function showMessage() {
alert('Hello from a function!');
}
</script>
<button onclick="showMessage()">Click me</button>
Here, when the button is clicked, it calls the showMessage() function, which then displays an alert box.
Things to remember: This attribute can be used with almost any HTML element, not just buttons.
It’s generally a good practice to separate your JavaScript from your HTML for better maintainability. This means instead of writing the script directly inside the attribute, you’d assign an ID to your element and then add an event listener in a separate <script> tag or external JavaScript file.
<button id="myButton">Click me</button>
<script>
document.getElementById('myButton').addEventListener('click', function() {
alert('Hello from an event listener!');
});
</script>
This attribute is a powerful tool that can be used to add interactivity to your web pages. By using the HTML button attribute, you can create web pages that respond to user input and provide a more engaging user experience.
HTML Onclick Attribute Impacts Website SEO
The onclick attribute itself does not have a direct impact on website SEO. Search engine algorithms are primarily concerned with content relevance, user experience, site speed, mobile-friendliness, backlinks, domain authority, and many other factors.
However, the way you utilize the attribute and JavaScript on your site can have indirect effects on SEO:
| Content Accessibility | If you use JavaScript to load essential content or links when an element with an onclick attribute is clicked, search engines might not see this content. If search engines can’t access or understand your content, it can’t be indexed or ranked. |
| User Experience (UX) | If you’re using the onclick attribute to enhance user experience, and it works effectively, it can indirectly benefit SEO. Better UX can lead to longer site visits, lower bounce rates, and increased user engagement, all of which can send positive signals to search engines. |
| Site Speed | Over-reliance on JavaScript, especially if not optimized, can slow down your website, especially if you have bulky scripts running due to onclick events. Site speed is a known SEO ranking factor, so it’s essential to ensure your site remains fast. |
| Mobile Experience | If your onclick events aren’t optimized for mobile devices, this can harm the mobile user experience, which is crucial for SEO, especially since Google uses mobile-first indexing. |
| Interactivity | With the introduction of Core Web Vitals by Google, metrics related to interactivity (like First Input Delay) have become a ranking factor. If your onclick handlers take too long to process or make the page unresponsive, it could negatively impact this metric. |
While the HTML button attribute itself doesnt affect SEO, the functionalities you implement with it can influence factors that search engines care about. Always prioritize the user experience, ensure content accessibility, and adhere to best practices when using JavaScript in your website’s design.
Troubleshooting and Solving Onclick Attribute Errors
Not Working At All
The onclick attribute isn’t triggering any action when clicked.
JavaScript Not Executing
The link with an onclick event is clicked, but the JavaScript is not executing or is producing unintended results.
Multiple Event Handlers
Multiple event handlers might interfere with each other, leading to unpredictable behavior.
JavaScript Disabled
The onclick functionality doesn’t work because JavaScript is disabled in the user’s browser.
Outdated JavaScript Libraries
The onclick function depends on a JavaScript library or framework that’s outdated or not loaded.
Mobile Devices Issues
The functionality works on desktop but not on mobile devices.
Event Bubbling or Propagation
The onclick event is being overridden or stopped due to event bubbling or propagation in nested elements.
Incorrect Element Targeting
The onclick event isn’t targeting the correct element due to dynamic content loading or other reasons.
By understanding these common onclick pitfalls and their solutions, developers can ensure a smoother user experience and avoid unexpected behaviors.
Href Overriding Onclick
If the link (<a>) has both an href attribute and an onclick event, the browser might navigate away before executing the JavaScript.
<a href="somepage.html" onclick="event.preventDefault(); doSomething();">Click me</a>Check Links With a URL in Onclick Attribute With Internal Link Checker by Sitechecker
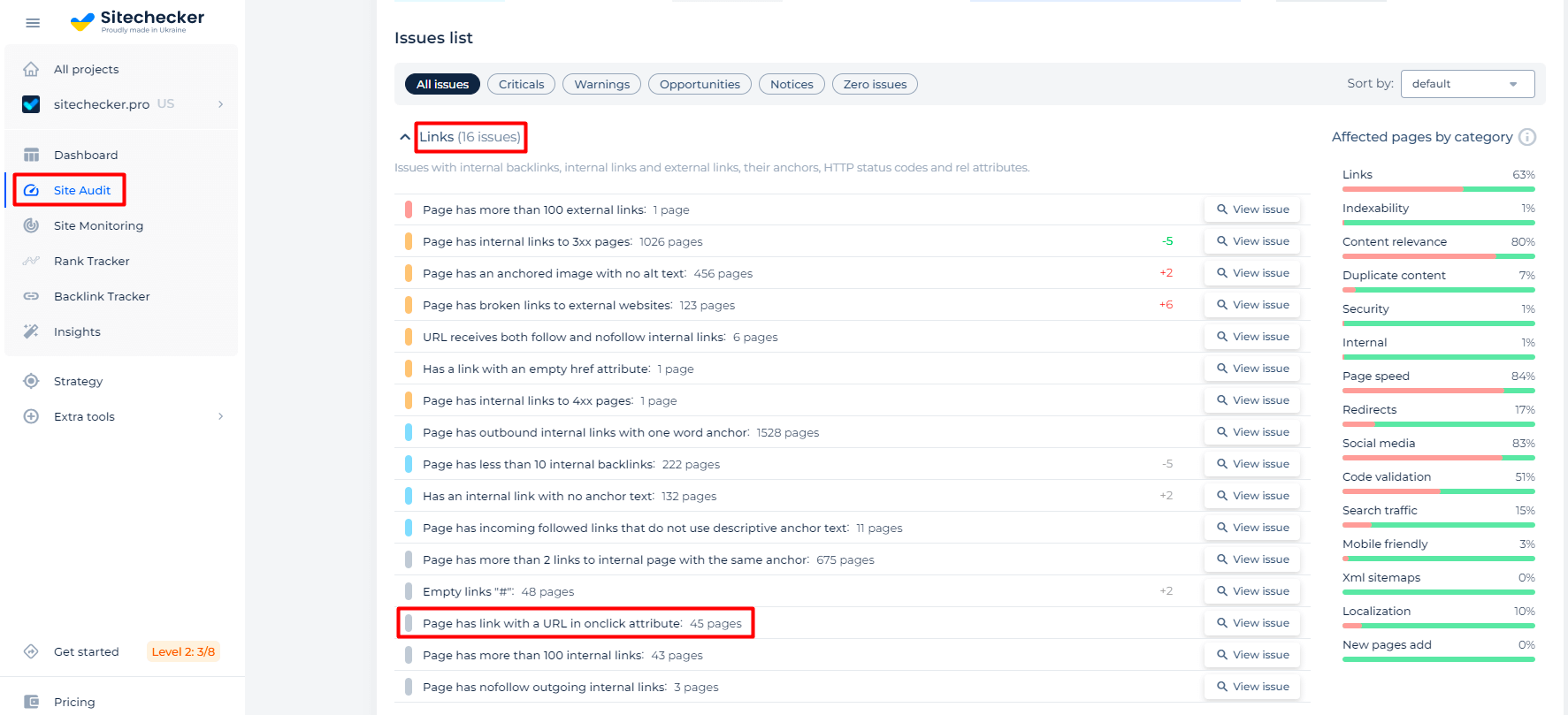
SiteChecker.Pro’s internal links tool offers a robust solution for webmasters and developers seeking to examine the intricacies of their website’s linking structure. One of the more nuanced issues in modern web development is the use of URLs within the “onclick” attributes of HTML elements. These are often employed to execute specific actions or navigate to different URLs when an element is clicked.
With SiteChecker.Pro, users can dive deep into their website’s architecture to identify and evaluate the efficacy and correctness of these onclick URLs. The tool scrutinizes every corner of the site, ensuring that even links embedded within JavaScript functions or dynamic actions are not overlooked. Such thorough examination is vital, especially since incorrectly implemented or broken onclick links can hinder user experience or disrupt intended website functionalities.
In essence, by leveraging SiteChecker.Pro’s capabilities, webmasters can ensure that their onclick attributes are correctly set up, pointing to the intended destinations, and functioning as desired. This aids in delivering a seamless and error-free browsing experience, vital for user satisfaction and engagement.
Conclusion
The HTML “onclick” attribute allows web developers to specify a JavaScript function that will execute when an HTML element is clicked, offering interactivity to web pages. While the attribute itself doesn’t directly affect SEO, the manner in which it’s implemented, combined with the JavaScript it calls, can indirectly impact essential SEO factors such as content accessibility, user experience, site speed, and mobile responsiveness. Additionally, webmasters need to be cautious of potential errors and conflicts with this attribute. Tools like SiteChecker.Pro provide a comprehensive solution to inspect and ensure the proper functioning of “onclick” attributes, particularly when they contain URLs, ensuring a smooth and optimal user experience.