HTML lang attribute missing issue means that website has pages where the <html lang=””> attribute is missing.
The Importance of the Issue
Despite Google and Yandex using hreflang to define local versions of the page, other search engines like Bing use the value set for HTML lang. The absence of HTML lang can lead to a failure in displaying the local version of the page.
<…>We don’t use that at all.
So we use the hreflang links if you have that if you have different language versions. But the language attribute within the HTML markup is something we don’t use at all. We’ve found that this language markup is something that is almost always wrong. So we tend to ignore that.<…>
John Muller, Senior Webmaster Trends Analyst at Google
If HTML lang is not set, the reading software uses the default language, which might cause a failure in displaying content. Source https://web.dev/html-has-lang/.
How to Check the Issue
Using any browser is enough to check the issue. Open the source code of the flawed page. To do this, click the right mouse button at any spot of the page and choose “browse the code” option, or apply an online tool https://codebeautify.org/source-code-viewer. Find a <html> tag and check if the lang attribute is present.
Example:
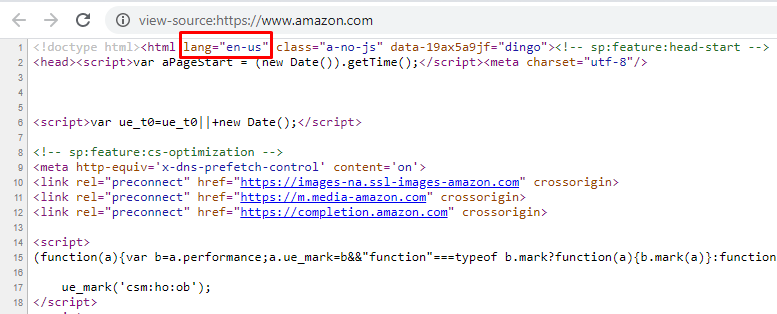
In the content relevance section of the Site Audit, Sitechecker tool is highlighting a widespread issue where pages are missing the HTML lang attribute. This attribute is crucial because it defines the language of your page, which is vital for search engines when categorizing and understanding the content, as well as for accessibility purposes, aiding screen readers to use the correct language pronunciation.
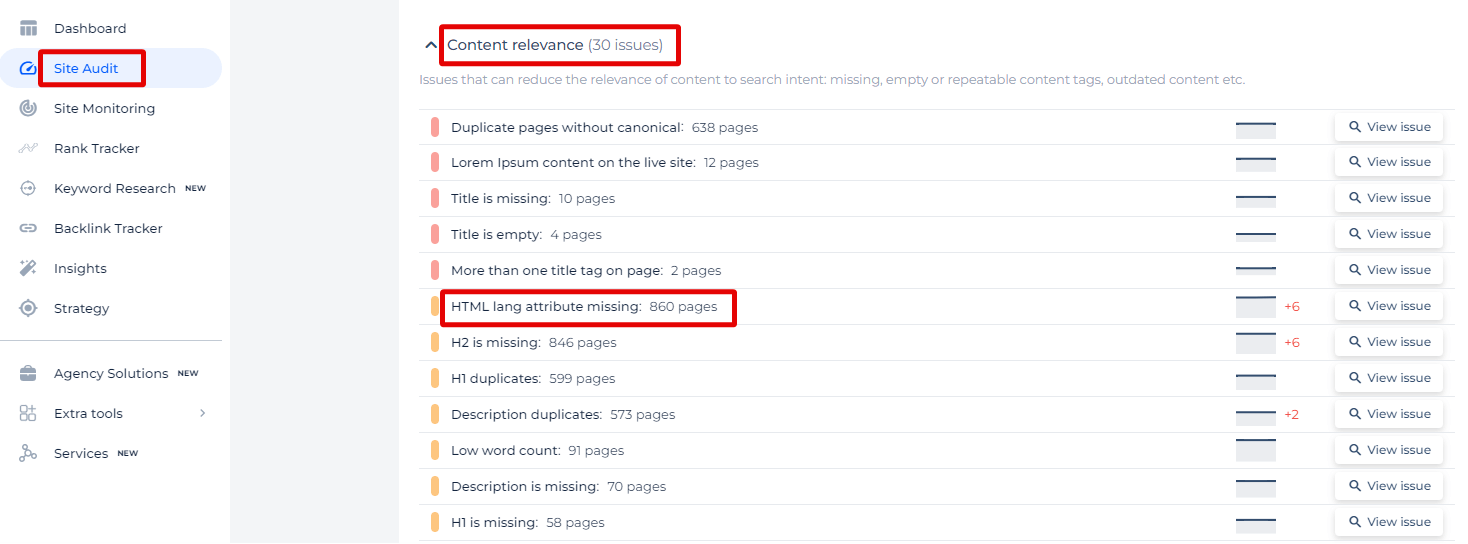
When the issue is opened, users are provided with a comprehensive list of all the URLs affected by this problem. Alongside each URL, additional details are available:
- Page Weight: This value, measured in a unit like kilobytes (not shown here but implied), signifies the size of the page which can impact load times.
- Status Code: The HTTP status code (like 200 for success) indicates the status of the URL when the site was crawled.
- Issue Found: This date confirms when the problem was detected by the Site Audit tool.
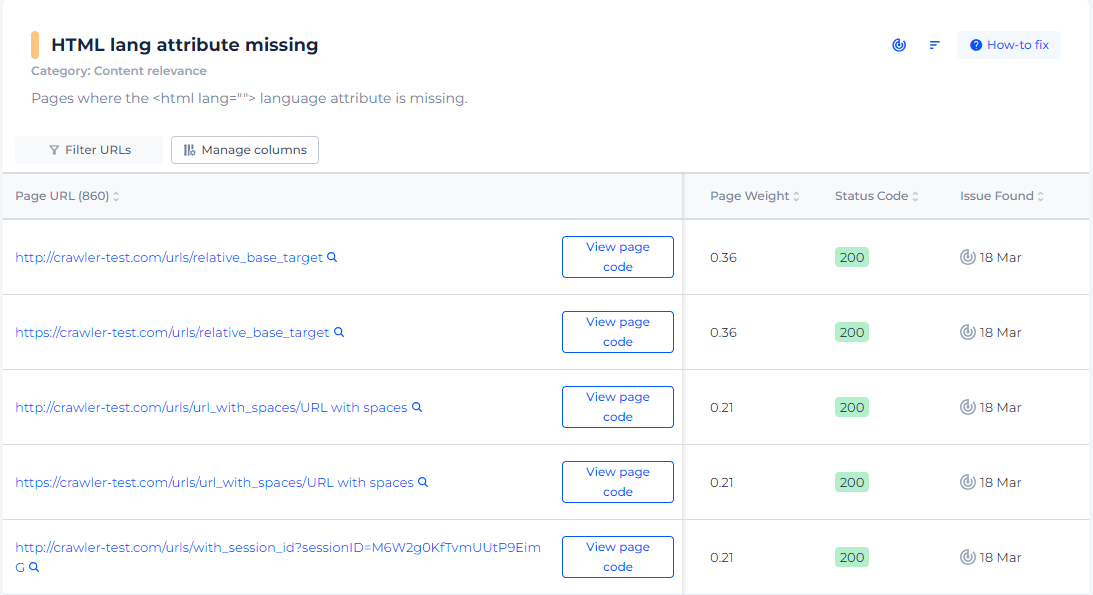
By clicking on “View page code,” users can directly access the page’s HTML code to pinpoint where the lang attribute should be added, allowing for a streamlined and efficient troubleshooting process.
Missing Lang Attributes? Find Them Fast!
Use our quick checker to find and fix these issues, and make every page on your site globally friendly.
How to Fix This Issue
1. Create a Plan for Fixing
Once you have a list of URLs, create a plan to fix them. This involves:
Determining the primary language of each page.
Deciding on the method of implementation (manual vs. automated).
2. Implement the Fixes
A. Manual Fixes
For a small number of pages, you can manually edit the HTML:
Open the Hypertext Markup Language file in a code editor.
Locate the <html> tag at the beginning of the document.
Add the language attribute with the appropriate language code. For example, for English:
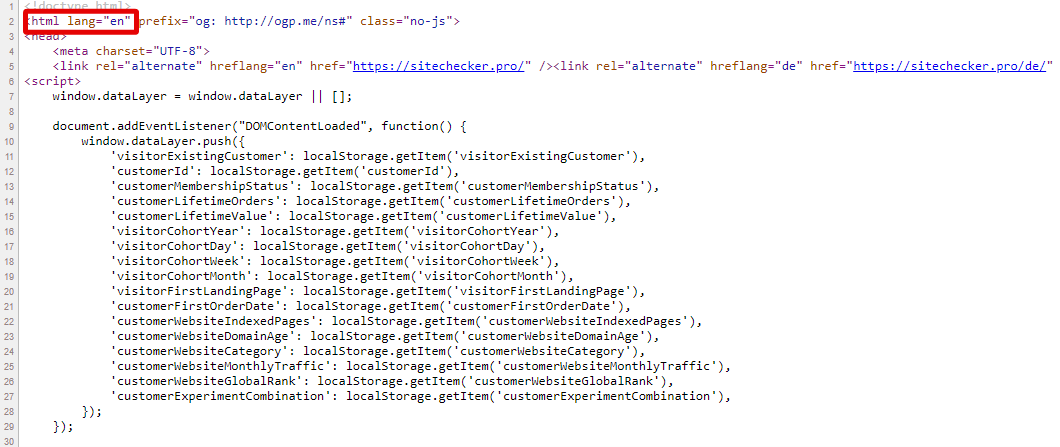
<html lang="en">
Save the document and upload it to your server if needed.
B. Automated Fixes
For a larger number of pages, automate the process using scripts. Below is an example using Python with the BeautifulSoup library:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import os
# Function to add lang attribute
def add_lang_attribute(file_path, lang='en'):
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
soup = BeautifulSoup(file, 'html.parser')
# Check if lang attribute is missing
if not soup.html.has_attr('lang'):
soup.html['lang'] = lang
# Write changes back to the file
with open(file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(str(soup))
# Directory containing HTML files
directory = 'path/to/html/files'
# Iterate through all files in the directory
for filename in os.listdir(directory):
if filename.endswith('.html'):
file_path = os.path.join(directory, filename)
add_lang_attribute(file_path, lang='en')
3. Validate the Fixes
After applying the fixes, validate that the language attribute has been correctly added:
Manual Check: Open a few files and check the HTML tag.
Automated Validation: Re-run the SEO audit to ensure the issue is resolved.
4. Monitor and Maintain
You should regularly monitor and maintain your web pages to ensure ongoing compliance. Schedule regular audits using Sitechecker to catch any new issues that might arise. If you use a Content Management System (CMS), ensure the templates include the lang attribute by default. By following these steps, you can effectively fix and maintain the lang attribute across all your web pages, ensuring better accessibility and SEO performance.