What is Page Speed?
Page Speed refers to the amount of time it takes for the content on a webpage to load fully. It’s the interval between the moment a user requests a new page and the moment the page is completely displayed on the screen. Page Speed is crucial as it’s one of the first interactions a user has with a website, and it can significantly impact user perceptions and experiences.
The Relevance of Page Speed in Web Browsing
Page Speed is paramount in web browsing because it directly influences user satisfaction and engagement levels. In today’s fast-paced digital world, users anticipate quick, seamless online experiences. A delay of even a few seconds can lead to frustration, causing users to abandon the site, which increases the bounce rate. Quick-loading websites, on the other hand, enhance user satisfaction, promote engagement, and encourage users to explore more content on the site.
High page speed also facilitates smoother navigation and interaction, allowing users to access information, complete tasks, and make purchases efficiently. This is especially pertinent for e-commerce websites, where user experience can directly affect sales and revenue.
The Significance of Page Speed for SEO
Page Speed is a critical factor in search engine optimization (SEO). It not only affects user experience but also influences how search engines rank websites. Search engines, like Google, aim to provide the best user experience possible, and therefore, prioritize websites that load quickly.
Impact on User Experience and Rankings
Slow-loading pages can significantly degrade user experience. Users are likely to leave a site if it takes too long to load, which increases bounce rates and reduces the average time spent on the page. These user behaviors are signals to search engines that the website might not be user-friendly, potentially leading to lower search engine rankings.
Conversely, websites with fast loading times are likely to have lower bounce rates and higher user engagement, sending positive signals to search engines. This can lead to better visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs), potentially driving more organic traffic to the site.
Here are some tweets from John Mueller about page speed:
Tweet 2:
Tweet 3:
The Role of Page Speed in Conversion Rates
Page speed is also crucial for maintaining high conversion rates on websites. Slow-loading pages can lead to user frustration, reducing the likelihood of users completing desired actions, such as making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a contact form.
Research has consistently shown a direct correlation between page speed and conversion rates. A fast, efficient, and user-friendly website encourages users to complete transactions, increasing the overall conversion rates. Conversely, every second of delay in page load time can result in a significant drop in conversions, adversely affecting the profitability of the website.
Core Web Vitals and Their Effect on Page Speed
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics introduced by Google to measure user experience on the web, focusing primarily on loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability. These vitals are integral as they give insights into the user experience and directly impact page speed, influencing both user satisfaction and SEO rankings.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures the time it takes for the largest content element visible in the viewport to fully load. This is critical as it provides an insight into the perceived load speed of the page from the user’s perspective. A good LCP score is below 2.5 seconds. Improving LCP can significantly enhance user experience as it ensures that the main content of the page is quickly visible to users, reducing wait time and frustration.
First Input Delay (FID)
First Input Delay (FID) quantifies the time from when a user first interacts with the page (like clicking a link or button) to the time the browser is actually able to respond to that interaction. A good FID score is less than 100 milliseconds. Optimizing for FID is crucial for enhancing interactivity and responsiveness, which in turn improves user satisfaction and engagement, especially for pages where users need to perform actions quickly.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures the amount of unexpected layout shift of visual page content. It is crucial for visual stability, and a good CLS score is below 0.1. High CLS can be frustrating for users as it may cause them to click on the wrong elements. Optimizing for low CLS ensures that page elements do not shift unexpectedly, providing a stable and reliable user experience.
Tools to Measure and Evaluate Page Speed
Optimizing page speed requires accurate measurement and evaluation, and several tools can help in assessing and improving page load times.
Website Speed Test by Sitechecker
Website Speed Test by Sitechecker provides a set of SEO and website performance tools, including a Website Speed Test that allows you to measure your webpage’s speed and receive recommendations for improvement.
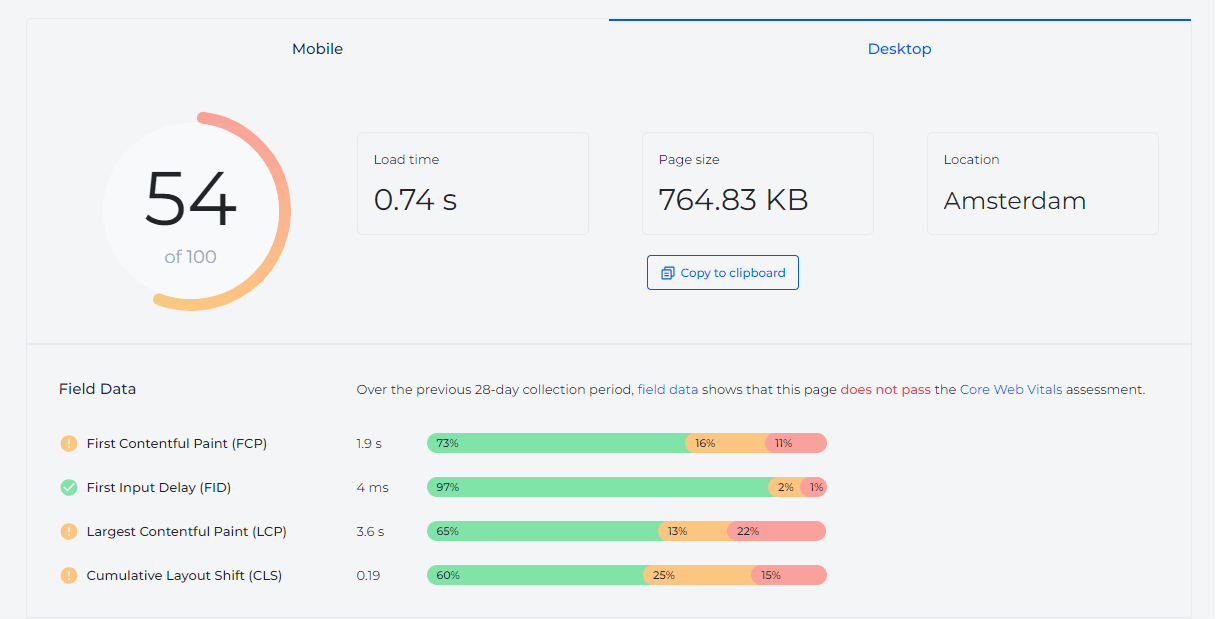
Google PageSpeed Insights
Google PageSpeed Insights is a widely-used tool that analyzes the content of a web page and then generates suggestions to make that page faster. It provides scores for both mobile and desktop versions and offers actionable recommendations for improvement.
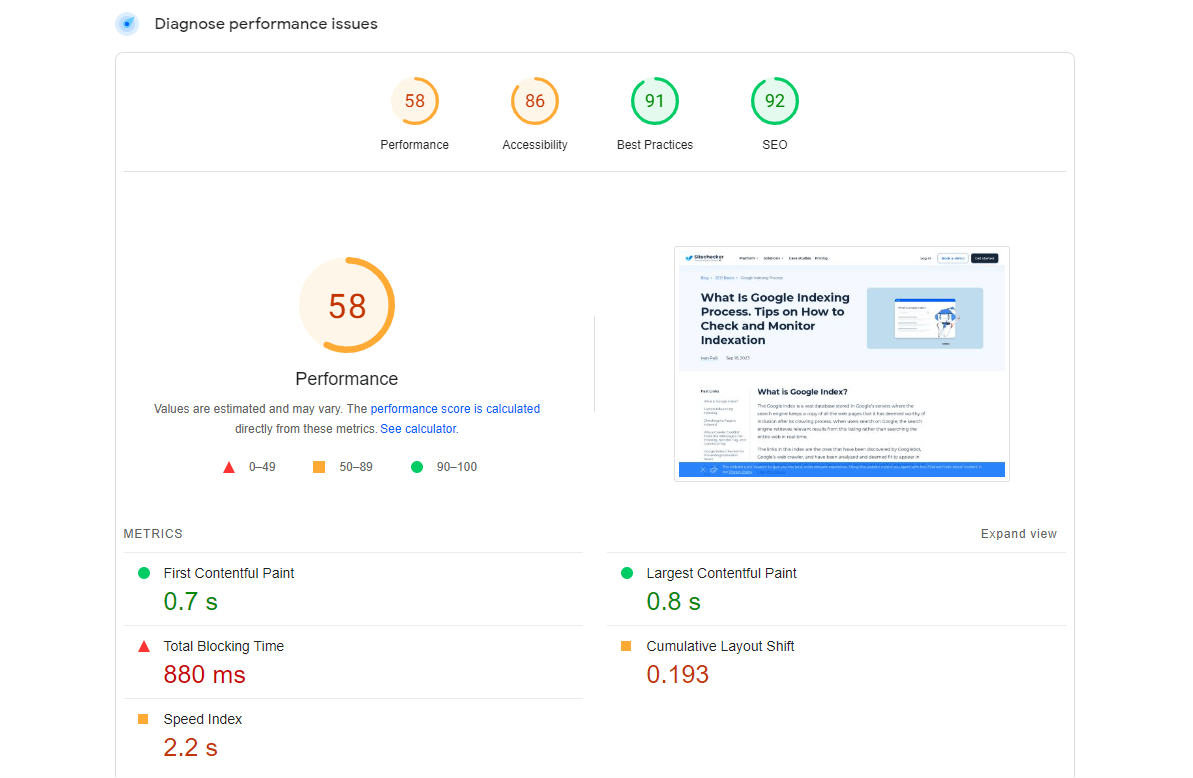
Google Lighthouse
Google Lighthouse is an open-source, automated tool for improving the quality of web pages. It has audits for performance, accessibility, progressive web apps, SEO, and more. It is extremely helpful in identifying performance bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement.
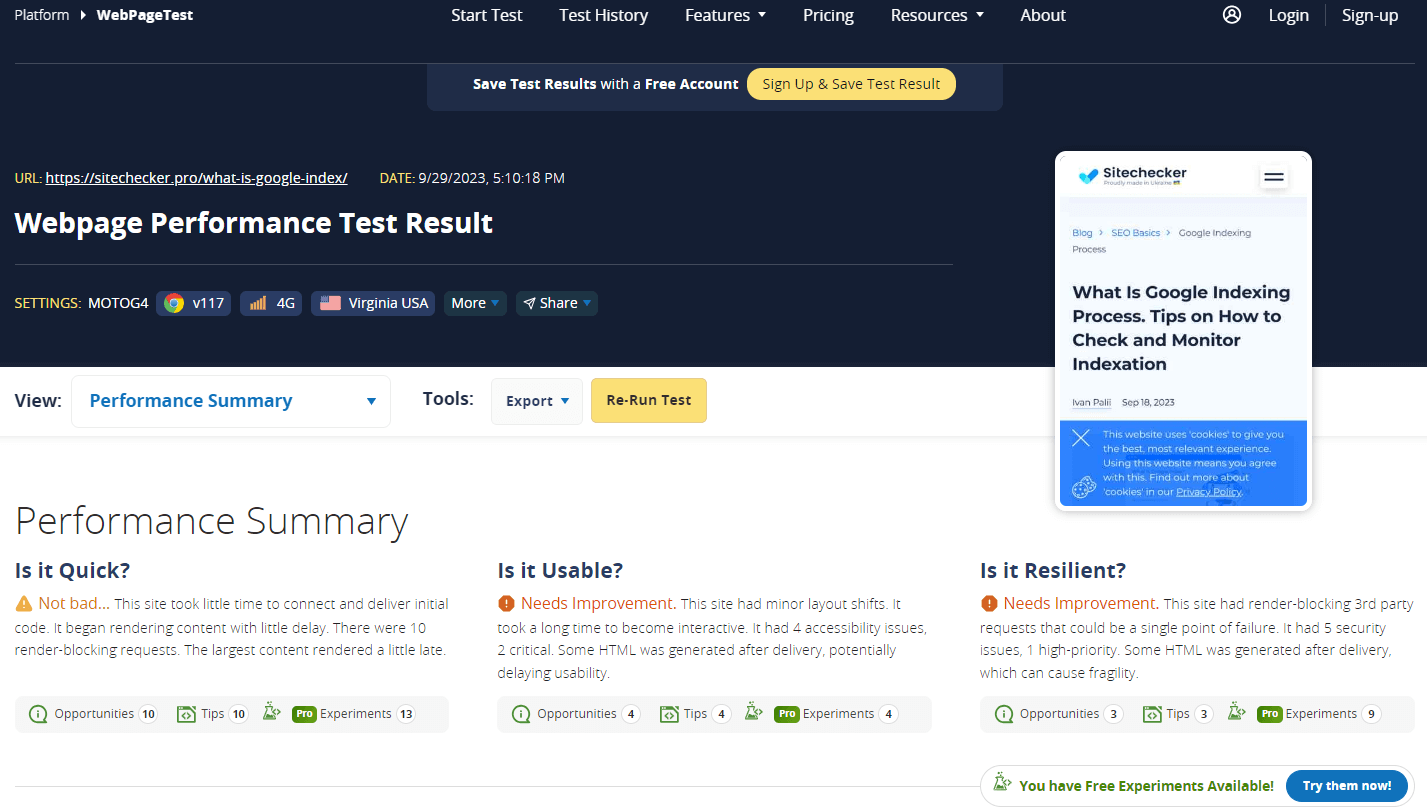
WebPage Test
WebPage Test allows you to run free website speed tests from multiple locations around the globe using real browsers (IE and Chrome) and at real consumer connection speeds. It provides detailed insights and a waterfall view of load times, allowing for in-depth analysis and optimization.
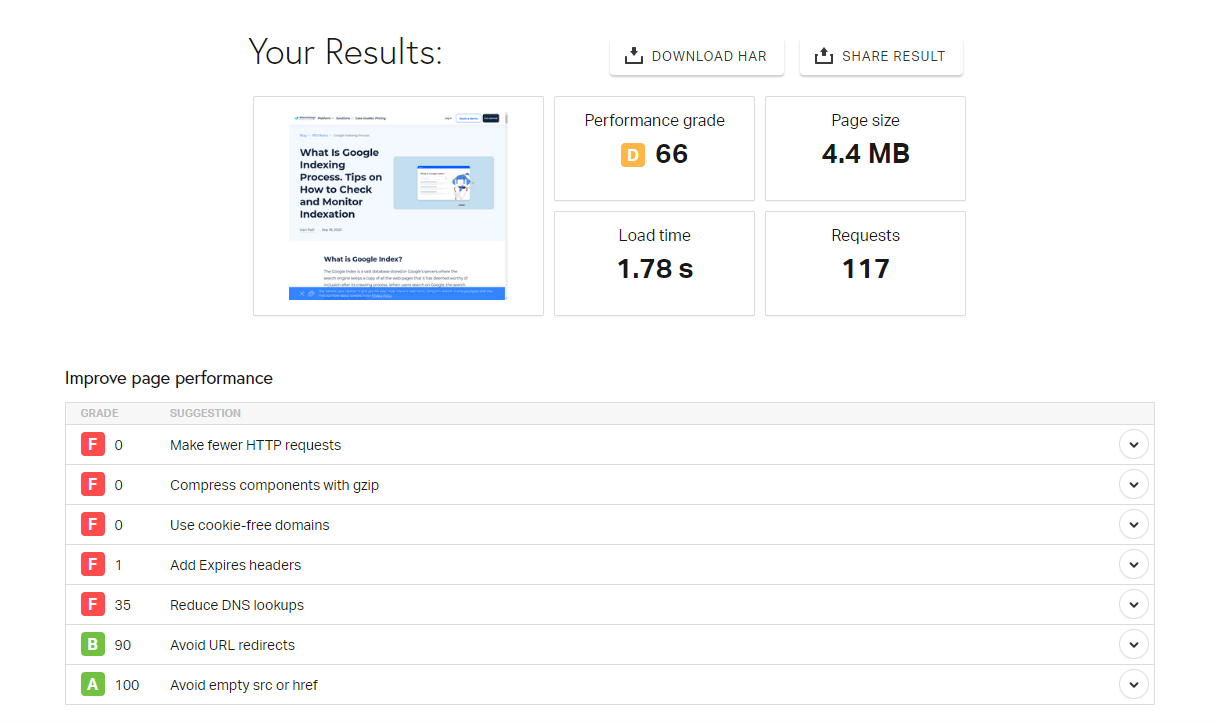
Pingdom Website Speed Test
Pingdom offers a suite of website monitoring tools, including a Website Speed Test, which allows you to test the load time of your web pages, analyze it, and find bottlenecks. It’s user-friendly and provides clear and actionable recommendations.
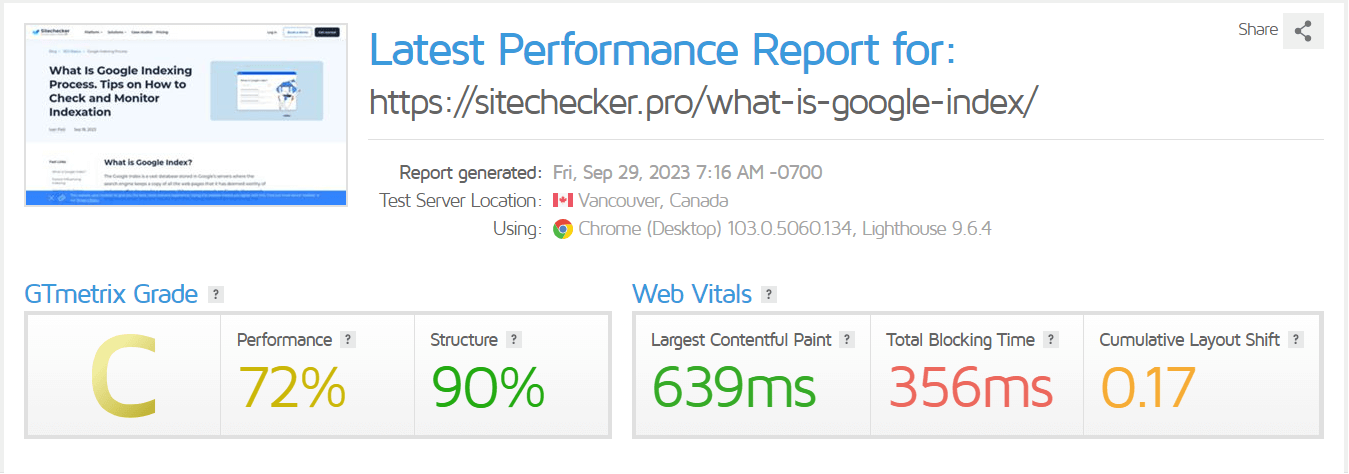
GTmetrix
GTmetrix is another popular tool that gives insights on how well your site loads and provides actionable recommendations on how to optimize it. It combines the results from Google PageSpeed Insights and YSlow to generate comprehensive website performance reports.
Best Practices to Optimize Page Speed
Optimizing page speed is crucial to improve user experience, enhance SEO rankings, and increase conversion rates. Employing best practices in optimizing page speed ensures a smoother and more engaging user experience. Below are some recommended best practices:
Compress and Optimize Your Images
Images are often the largest files on a web page and can significantly affect page load time. Compressing and optimizing images can drastically reduce their file size, improving page speed without compromising on quality.
Choosing the Right Image Format
Selecting the appropriate image format is crucial. JPEG is best for photographs and images with gradients, PNG is suitable for transparent and high-quality images, and GIF is ideal for animations. WebP is a newer format that provides superior compression and quality characteristics, making it a good choice for web images.
Utilizing Image Compression Tools
Several online tools and software can help in compressing images without degrading quality. Tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, and Compressor.io can reduce image file sizes significantly, leading to faster page load times.
Minimize HTTP Requests
Each component on a page, such as scripts, images, and stylesheets, requires an HTTP request to the server, and too many requests can slow down page load times. Reducing the number of components and minimizing HTTP requests can optimize page speed.
Limiting the Use of Plugins
Every plugin requires resources to run, and having too many can create unnecessary HTTP requests, slowing down your website. Evaluate your plugins and keep only those that are essential, deactivating or deleting any that are unnecessary or redundant.
Streamlining External Scripts
External scripts, such as ads, font loaders, and other third-party scripts, can also increase the number of HTTP requests. Streamlining or asynchronously loading external scripts can help in minimizing HTTP requests, optimizing page load times.
Minify JavaScript, CSS, and HTML Files
Minifying JavaScript, CSS, and HTML files is an effective method for improving page speed. Minification involves removing unnecessary characters from code files, such as whitespace, new line characters, and comments, without altering functionality. This reduces file sizes, allowing faster download times and improved page load speeds. Various tools and plugins can automate the minification process, making it easier to implement and maintain.
Leverage Browser Caching
Browser caching allows frequent visitors to your site to store cached versions of static resources, reducing the load on your server and speeding up page load times for the user. By specifying an expiration date for your resources, you can control how long browsers should keep images, CSS, and JavaScript stored locally. Effective browser caching not only enhances user experience by rendering pages faster but also reduces server load, benefiting overall website performance.
Utilize a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a network of servers distributed across various locations worldwide, allowing users to download resources from the nearest server. CDNs are instrumental in delivering content rapidly to users, minimizing latency and packet loss, especially for websites with a global audience or high traffic volumes.
Benefits of a CDN
Using a CDN offers several advantages. It reduces the load on the origin server, decreases website load times, and enhances user experience, especially for users located far from the origin server. CDNs also improve website security by providing DDoS protection and other security features.
Choosing the Right CDN Provider
When selecting a CDN provider, consider factors such as network infrastructure, server locations, cost, security features, and customer support. Providers like Cloudflare, Akamai, and Amazon CloudFront offer robust CDN services catering to diverse needs. Evaluating your website’s requirements and choosing a provider that aligns with your objectives is crucial for maximizing the benefits of CDN implementation.
Technical SEO and the Interplay with Page Speed
Technical SEO refers to optimizing your site for the crawling and indexing phase, ensuring search engines can access, crawl, interpret, and index your website without any problems. Page speed is a crucial component of technical SEO as it directly affects user experience and search engine ranking. Below are some key elements of technical SEO that, when optimized, can enhance page speed and overall site performance.
Secure and Accessible Website
Having a secure and accessible website is the foundation of technical SEO. Utilizing HTTPS by acquiring an SSL certificate ensures data on your site is encrypted, building user trust and improving site rankings. Ensuring your website is accessible to search engines by creating a well-structured, clean, and well-organized sitemap enables easier crawling and indexing, contributing to improved visibility and higher SEO rankings.
SEO-Friendly URLs
Creating clear, concise, and SEO-friendly URLs is essential for both users and search engines. Descriptive URLs give users and search engines an immediate indication of the page content and are more likely to be clicked on. Incorporating relevant keywords, using hyphens to separate words, and avoiding unnecessary characters and words can make URLs more SEO-friendly, aiding in better indexing and ranking of the pages.
Mobile Optimization: Elevating User Experience and SEO Rankings
Given the surge in mobile usage, optimizing websites for mobile devices has become a cornerstone in enhancing user experience and SEO. Mobile optimization ensures that mobile users experience equivalent functionality and ease of use as desktop users. It’s not just a user-centric practice; it is a pivotal factor affecting SEO rankings, given Google’s mobile-first indexing. Below are aspects and strategies of mobile optimization that merit a deeper exploration:
| Component | Definition | Benefits | Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) | An open-source framework designed to make mobile pages load faster by simplifying HTML, leveraging optimized CSS, and loading resources asynchronously. | – Enhanced Page Speed: Improved user experience and reduced bounce rates on mobile devices. – Increased Visibility: Prioritization in Google search results, possibly leading to increased visibility and click-through rates. – Improved User Engagement: Provides a fast, smooth, and responsive user experience. | To create an AMP version of a webpage, use the AMP HTML framework, incorporating AMP-specific tags and minimizing unnecessary elements and scripts. |
| Responsive Design | Ensures that the website’s layout and content adapt seamlessly to different screen sizes, providing an optimal viewing experience across various devices. | – Flexibility: Allows the web page to look and function well on any device. – Improved User Experience: Eliminates the need for pinching and zooming, allowing more comfortable navigation and content consumption. – Enhanced SEO Rankings: Contributes to better SEO rankings due to Google’s preference for mobile-friendly websites. | Employ flexible grids, scalable images, and media queries to develop a responsive design. Media queries apply different styles based on the device characteristics, ensuring an optimal user experience on any screen size. |
| Mobile-Friendly Design Elements | Integral components that enhance usability on mobile devices, such as readable text, easy navigation, and accessible call-to-action buttons. | – User-Centric Approach: Ensures smoother, more intuitive user experience catering to the preferences and behaviors of mobile users. – Reduced Bounce Rate: Reduces friction and frustration, potentially lowering bounce rates and elevating user engagement levels. | Utilize legible font sizes, ensure tap targets are appropriately sized and spaced, optimize content layout, and prioritize succinct, clear, and compelling call-to-actions. |
Guide to Implementing Page Speed Optimization Strategies
To implement page speed optimization strategies, here are detailed step-by-step solutions for leveraging browser caching and minifying code, two critical components in enhancing page speed.
1. Leveraging Browser Caching
Browser caching allows storing of webpage resource files on a local computer when a user visits a webpage. Here’s how to leverage browser caching:
Step 1: Access .htaccess File
Locate and access the .htaccess file on your web server, typically found in the root directory.
Step 2: Modify .htaccess File
Add the following lines to your .htaccess file to set the expiry times.
ExpiresActive On
ExpiresByType image/jpg "access 1 year"
ExpiresByType image/jpeg "access 1 year"
ExpiresByType image/gif "access 1 year"
ExpiresByType image/png "access 1 year"
ExpiresByType text/css "access 1 month"
ExpiresByType text/html "access 1 month"
ExpiresByType application/pdf "access 1 month"
ExpiresByType text/x-javascript "access 1 month"
ExpiresByType application/x-shockwave-flash "access 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/x-icon "access 1 year"
ExpiresDefault "access 1 month"
Adjust the access parameter to fit your needs, controlling how long browser caching is active.
Step 3: Save and Upload
Save the .htaccess file and upload it back to your web server if necessary.
Step 4: Test
Test your website to ensure that the changes are working correctly. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to verify that browser caching is effectively implemented.
2. Minifying Code
Minifying code involves removing unnecessary characters from your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files to reduce their size. Here’s how to minify code:
Step 1: Identify Files to Minify
List out the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files that are a part of your website’s design.
Step 2: Use Online Minification Tools
Use online tools like CSS Minifier, JavaScript Minifier, or HTML Minifier to minify your code.
Simply copy-paste your code into these tools, and they will provide a minified version.
Step 3: Replace Original Files
Replace the original files on your server with the minified versions.
It is advisable to keep a backup of the original files in case you need to modify them in the future.
Step 4: Test Website
After replacing the files, thoroughly test your website to ensure there are no layout issues or functionality loss.
Step 5: Monitor Performance
Regularly monitor your website’s performance using Page Speed Insights or other similar tools to ensure optimal load times and immediately address any issues that arise.
Sitechecker’s Speed Test to Monitor Your Website’s Performance
The Website Speed Test tool is a comprehensive solution designed to analyze your website’s loading speed and efficiency. Speed is pivotal for user experience and SEO, and this tool provides detailed insights into elements impacting your site’s performance. By inputting your URL, you receive a meticulous breakdown of improvement areas, allowing you to enhance your site’s speed and overall user satisfaction, which is crucial in today’s fast-paced digital environment.
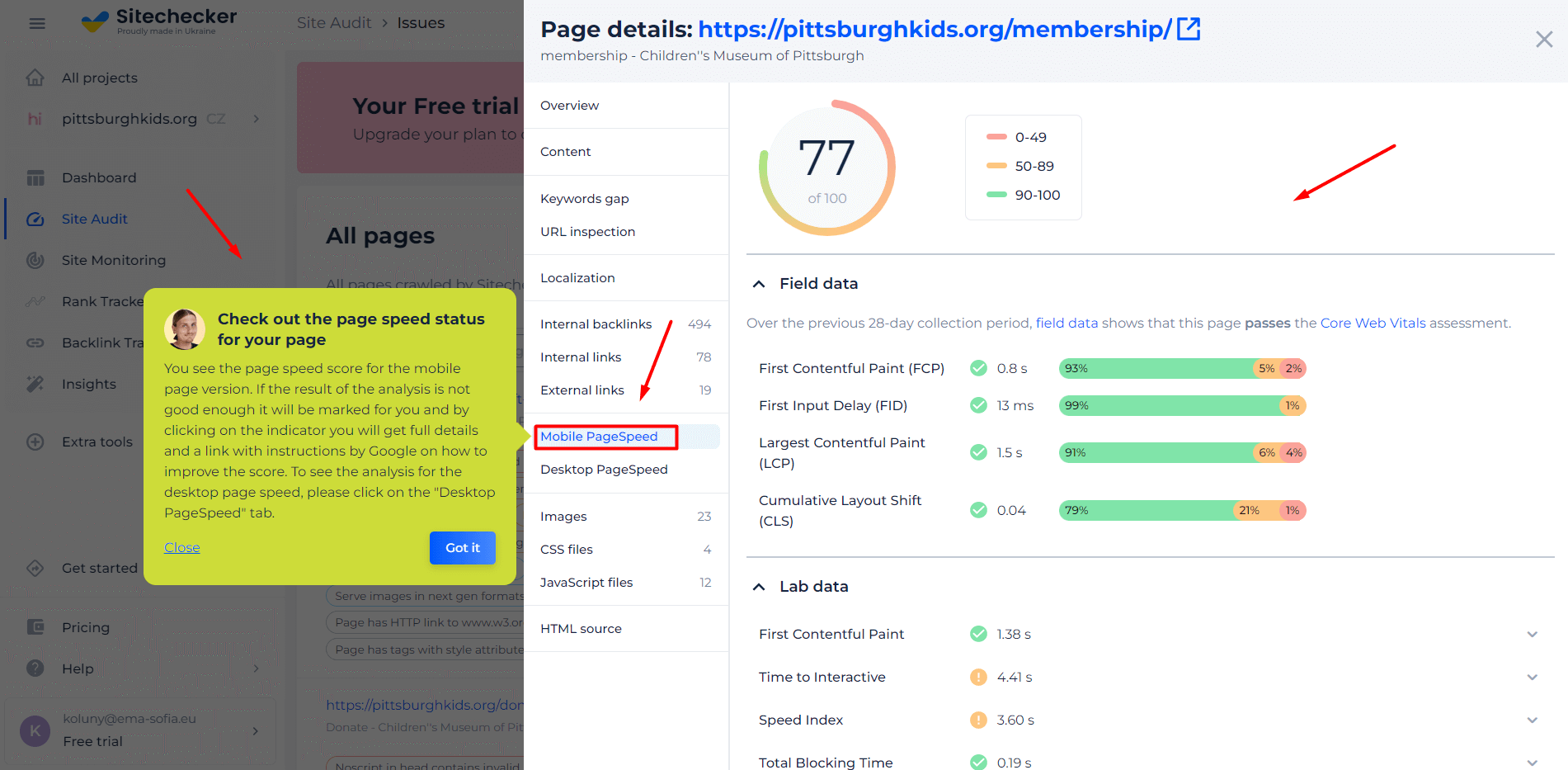
With its user-friendly interface and precise recommendations, this tool is indispensable for website owners aiming for optimum functionality and user engagement. It demystifies the complexities behind page speed, offering actionable insights to elevate your website’s performance and search engine ranking. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or a beginner, the Website Speed Test tool is a valuable asset in your optimization arsenal.
Unlock Peak Website Performance!
Discover what's holding you back and optimize for the best user experience.
Summary
In conclusion, technical SEO is pivotal for enhancing page speed and overall website performance. Incorporating mobile optimization, maintaining a secure and accessible website, and utilizing SEO-friendly URLs are key strategies to improve user experience and boost search engine rankings. Page speed is integral within this optimization, acting as a direct influencer of user satisfaction and SEO performance. A holistic approach, focusing on both technical SEO aspects and page speed, ensures a well-rounded, efficient, and high-performing website that meets user needs and search engine requirements.
Regular audits and refinements are essential to maintain optimal performance in the constantly evolving digital landscape.