What Does «Base URL Malformed or Empty» Mean?
The error message “Base URL Malformed or empty” indicates that the root address provided in a web request or configuration is either incorrectly formatted or not specified at all. Here’s a breakdown of what each part means:
Base URL
This is the primary address used to make requests in a web application or API. For example, in the link https://example.com/api/v1, the base URL is https://example.com.
Malformed
This suggests that the URL does not conform to the standard link structure. This could mean that it lacks essential components such as the protocol (http:// or https://), has invalid characters, or has an incorrect syntax.
Empty
This means that the base URL is missing altogether. The application or configuration file expects a root address to be specified, but it finds an empty string or null value instead.
What Triggers This Issue?
The “Base URL Malformed or empty” issue is triggered by several common factors:
- Typographical Errors: Mistyped characters or missing protocol (e.g., http://).
- Incorrect URL Format: hyperlinks missing essential parts, like the protocol.
- Configuration Issues: Base URL not set or improperly set in configuration files or environment variables.
- Programmatic Errors: Code incorrectly generating or handling the root address. Uninitialized variables used for the base URL.
- Deployment Issues: Incorrect environment-specific configurations during deployment.
- User Input Errors: Users providing incomplete or incorrect addresses.
How to Check the Issue?
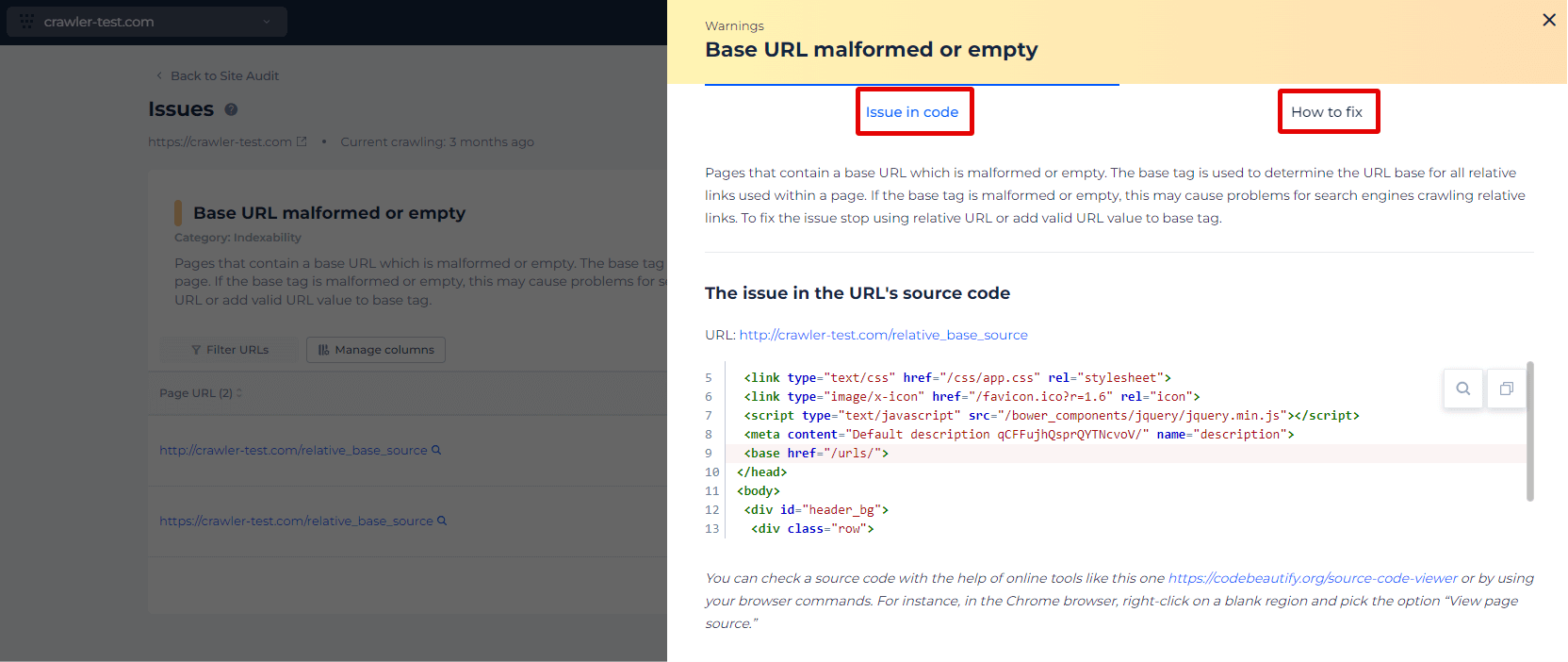
The href attribute of the tag should contain the URL without errors.
URL example:
<base href="https://site.com/resources/images">When you use it to link to the document picture-1.jpg you can just type
<img src="images/picture-1.jpg">Examples of an incorrect base tag
The path to the document folder is not specified:
<base href = "">An invalid protocol is specified in the base URL:
<base href = "htps://site.com">The base URL contains spaces:
<base href = "https://site. com">For browser compatibility, check out the guide for developers: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/base.
Forget about this problem with our tool. Sitechecker detects all pages with base URL malformed or empty, so you can easily fix them.
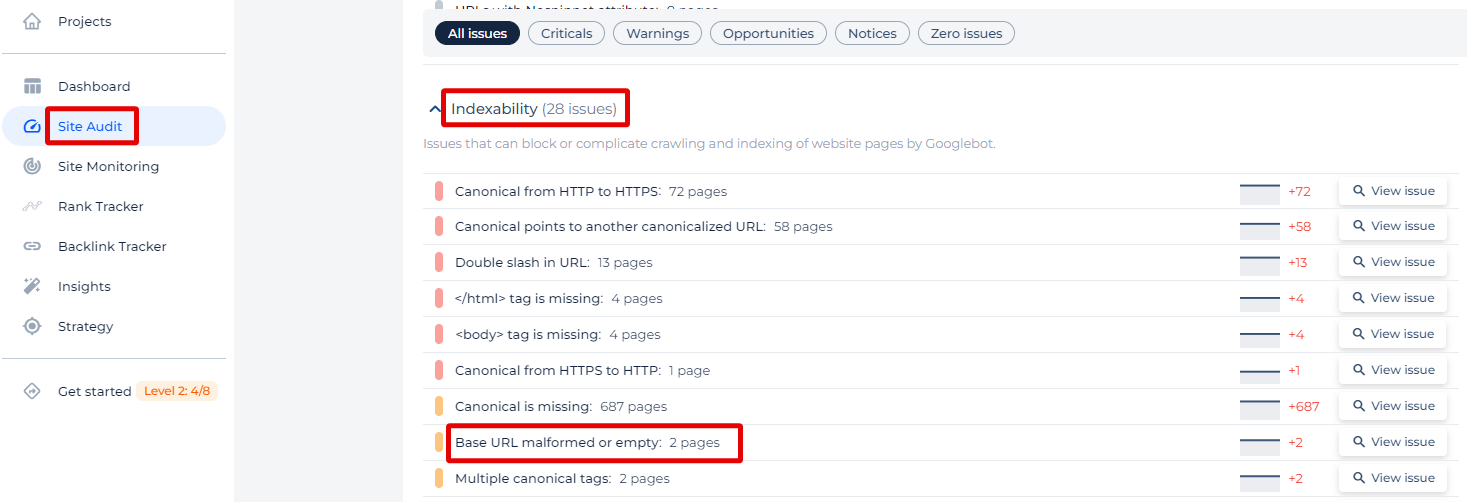
Right in the app, you can check the issue in code and find some valuable advice on how to fix the problem.
Optimize Your Website's Core - Fix Base URL Errors!
Sitechecker Audit Tool effortlessly checks and helps to rectify any Base URL issues.
How to Fix the Issue?
To fix the “Base URL Malformed or empty” issue, follow these steps:
1. Check URL Syntax
Ensure the root address is correctly formatted and includes the protocol (e.g., https://example.com).
Verify there are no typos or misplaced characters.
2. Review Configuration Files
Ensure the base URL is properly set in your configuration files or environment variables.
Replace placeholders (e.g., {{BASE_URL}}) with actual values.
3. Inspect and Correct Code
Check the parts of your code that generate or manipulate the base URL.
Ensure the root address variable is initialized and assigned correctly.
base_url = "https://example.com" # Ensure this is set correctly
if base_url:
complete_url = base_url + "/api/v1/endpoint"
4. Deployment Process
Verify that environment-specific configurations are correctly set during deployment.
Check deployment scripts for proper setting of the root address.
5. Validate User Input
Implement input validation to ensure users provide complete and correct addresses where necessary.
Example Fixes
1. Correct URL Format
htps://example.com --> https://example.com
2. Proper Configuration Setting
{
"baseUrl": "https://example.com"
}
3. Code Initialization
base_url = "https://example.com" # Properly set base URL