What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to the practice of optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. It encompasses both the content on that web page as well as the HTML source code. Key elements include, but are not limited to, keyword optimization, meta descriptions, HTML tags, and internal links. On-page SEO ensures that your content and its presentation are of the highest quality and relevance for both search engines and users.
What’s the Difference Between On-Page SEO and Off-Page SEO?
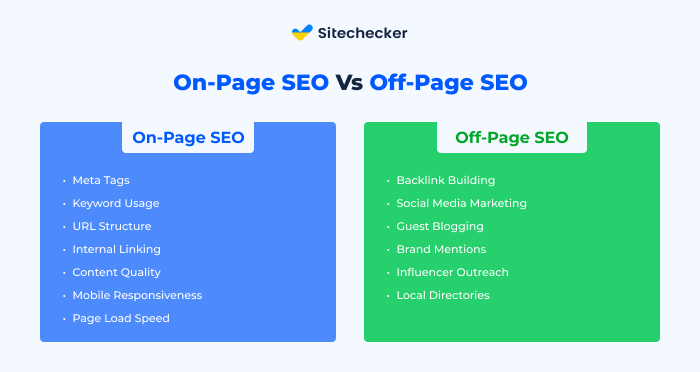
While on-page SEO pertains to the optimizations you can control directly on your website, off-page SEO revolves around external factors that influence your website’s authority and reputation. Common off-page strategies include link building from reputable other websites’, social media engagement, and other marketing efforts outside of your own website.
In simple terms, on-page SEO focuses on what your site is about, ensuring it’s optimized for relevant keywords and provides a great user experience. In contrast, off-page SEO is about how authoritative and popular your site is, which is determined by what other sites say about you. Both are crucial for a well-rounded SEO strategy.
Why is On-Page SEO Important?
On-page SEO is a cornerstone in ensuring a website’s visibility and success in the digital landscape. Its significance can be attributed to several key reasons:
| Relevance to Search Queries | Proper on-page SEO ensures that your content is optimized for specific keywords and phrases. This helps search engines understand the context of your pages and makes it more likely for your site to appear when users search for related terms. |
| Improved User Experience | Good on-page SEO practices, such as clear headings, optimized images, and structured content, enhance the user experience. A site that’s easy to navigate and understand will likely keep visitors engaged for longer periods. |
| Higher Search Rankings | Pages that are well-optimized stand a better chance of achieving higher positions in search engine results. A higher ranking often translates to increased visibility and more organic traffic. |
| Maximizing Organic Traffic | With the continual rise in advertising costs, relying on organic traffic becomes even more valuable. Effective on-page SEO attracts targeted organic traffic, which tends to convert better than paid traffic. |
| Supporting Off-Page Efforts | While off-page SEO focuses on external signals like backlinks, having solid on-page optimization ensures that the quality of your content and its presentation can effectively leverage those external signals. |
| Adapting to Search Engine Changes | Search engines are always evolving, and their algorithms change frequently. A strong foundation in on-page SEO makes it easier to adapt to these changes and maintain or improve rankings. |
| Increasing Click-Through Rates | Elements of on-page SEO, like meta titles and descriptions, directly impact the way your site is presented in search results. Compelling titles and descriptions can significantly improve click-through rates from search engine results pages. |
In summary, on-page SEO is not just about appeasing search engines but also about providing valuable and relevant content to users. It’s a strategic combination of technical optimization, quality content, and user-focused strategies that collectively enhance a website’s online visibility and performance.
On-Page SEO Elements
On-page SEO encompasses a myriad of elements that, when optimized effectively, play a crucial role in improving the visibility, usability, and performance of a webpage. Here’s a detailed overview:
Content Elements
Keyword Optimization: Ensuring that keywords are appropriately integrated into your content, headers, and meta tags without over-optimizing.
Content Quality: Publishing high-quality, original, and relevant content that offers value to readers and answers their queries.
Content Freshness: Regularly updating content and ensuring that it remains current and relevant.
Visual Content: Integrating images, infographics, and videos that are optimized for loading speed and have appropriate alt tags.
HTML Elements
Page Titles: Crafting unique and descriptive titles for each page that incorporates target keywords.
Headers: Using header tags (H1, H2, etc.) appropriately to structure content and highlight key points.
Meta Descriptions: Writing compelling meta descriptions that accurately summarize the content of the page and encourage click-throughs from search engine results pages.
Image Alt-text: Adding descriptive alt text to images, making them accessible and helping search engines understand their context.
Structured Markup (Schema Markup): Implementing structured data to provide search engines with more detailed information about the content of your pages.
Site Architecture Elements
Page URLs: Constructing descriptive, concise URLs that incorporate keywords and are easily understandable by both users and search engines.
Internal Linking: Strategically linking to other relevant pages within your website to help users navigate and spread page authority.
External Linking: Linking out to authoritative, trustworthy external sources can bolster the credibility of your content.
Mobile Responsiveness: Ensuring that your website is optimized for mobile devices, offering a seamless user experience across all devices.
Site Speed: Optimizing page load times by compressing images, leveraging browser caching, reducing server response times, and other tactics.
User Engagement and Experience
Interactive Elements: Adding features like polls, quizzes, or interactive infographics to engage users.
Navigation: Ensuring that your site’s navigation is intuitive and user-friendly, allowing visitors to easily find the information they’re seeking.
Page Layout: Designing pages with a clean, organized layout that enhances readability and user experience.
In essence, on-page SEO elements form the foundation of your website’s search engine performance. By optimizing these elements, you ensure that both search engines and users can easily find, understand, and engage with your content.
Content Elements
Content is the backbone of any webpage. The way it’s presented on page elements, its quality, and its relevance to the target audience can significantly influence how well a page performs in search engine rankings. Here are the key content elements that need attention in on-page SEO:
-
Keyword Optimization: This involves understanding what keywords or phrases your target audience is using to find content and integrating those terms naturally into your content. Proper keyword optimization involves:
Primary Keywords: Main terms that directly relate to the topic.
Secondary Keywords: Variations or related terms to the primary keywords.
Long-tail Keywords: Longer, more specific phrases that visitors might use.
-
Content Quality: The essence of any page is the value it offers its readers. High-quality content is:
Original (not duplicated from elsewhere).
Relevant to the target audience.
Informative and provides a solution or answer to user queries.
- Content Freshness: Search engines favor content that is regularly updated and remains current. Regularly revisiting and updating content ensures it remains accurate, relevant, and offers the latest information.
-
Visual Content: Images, videos, infographics, and other visual aids enhance the user experience, break up text, and can provide additional context or information. Key considerations include:
Image Optimization: Using appropriate file formats, compressing for web without losing quality, and ensuring fast load times.
Alt Text: Providing descriptive alt text for every image, which helps search engines understand the image’s context and improves accessibility for users with screen readers.
Video Transcripts: If using videos, offering transcripts can boost SEO by providing search engines with readable content.
- Content Structure: Breaking content into easily digestible sections, using headings, subheadings, bullet points, and short paragraphs, aids readability and allows search engines to understand the structure of your content.
- Content Depth: While it’s not always about length, comprehensive content that covers a topic in depth can be seen as more authoritative and valuable to users.
- Call-to-Action (CTA): Engaging content often ends with a compelling CTA, guiding users on what action they should take next, be it reading another article, signing up for a newsletter, or making a purchase.
In summary, the content elements of on-page SEO ensure that your content not only appeals to search engines but also genuinely engages and provides value to your audience. By focusing on these elements, you create a foundation for a webpage that’s optimized for both visibility and user satisfaction.
1. Write Unique, Helpful Content
Creating original content that isn’t replicated from elsewhere is essential for SEO. Unique content:
- Establishes your site’s authority and expertise in a subject matter.
- Offers value to your readers, enhancing user engagement and time spent on the site.
- Reduces the risk of search engine penalties for duplicate content.
2. Keyword Research
Keyword research is the foundation of SEO content creation. It involves:
- Identifying words and phrases that potential customers use to search for content.
- Analyzing search volume and competition to determine which keywords are worth targeting.
- Understanding user intent behind keywords to tailor content accordingly.
3. Visual Content
Incorporating images, videos, and infographics can significantly enhance user experience and engagement. For effective visual content:
- Use high-quality images and videos that complement the written content.
- Ensure images are optimized for web to decrease loading times.
- Use relevant captions and descriptive filenames.
HTML Elements
These are elements within a webpage’s source code that can be optimized for search engines. Properly structured and optimized HTML elements enhance the search engine’s understanding of web page content.
4. Page Titles
The title of a page, often displayed in search results, is crucial for user click-through and search engine interpretation. Effective page titles:
- Are concise yet descriptive.
- Incorporate the primary keyword or phrase for the page.
- Reflect the content accurately.
5. Headers
Headers (H1, H2, H3, etc.) structure content and make it more readable. They also give search engines an idea of the content’s hierarchy and importance. Headers should:
- Be used sequentially (i.e., H1 followed by H2, then H3).
- Include relevant keywords where natural.
- Summarize the content they precede.
6. Meta Descriptions
Though not a direct ranking factor, meta descriptions can influence click-through rates. These brief summaries of a page’s content:
- Should be compelling and accurate.
- Can include relevant keywords.
- Are ideally between 150-160 characters.
7. Image Alt-text
Alt text describes the appearance and function of an image on a page, aiding accessibility and offering search engines a textual description of visuals. Effective alt text:
- Is concise yet descriptive.
- Includes relevant keywords without keyword stuffing.
- Describes the image’s content and purpose.
8. Structured Markup (Schema Markup)
Schema Markup helps search engines better understand the context of content. By adding this to your HTML, you can enhance the way your page displays in search results with rich snippets. Structured Markup:
- Can be used to define articles, reviews, events, and more.
- Enhances search visibility with rich results.
- Requires adherence to the specific schema.org guidelines for formatting.
By optimizing these elements, you can improve the visibility of your content in search engines, enhance user experience, and increase the likelihood of achieving higher rankings.
Site Architecture Elements
A well-structured site architecture aids both search engines in crawling and indexing your site efficiently and users in navigating your content seamlessly. Here are the key elements that form the foundation of an effective site architecture:
9. Page URLs
Page URLs, or web addresses, play an integral role in site architecture and SEO:
Descriptive and Readable: Good URLs succinctly describe the content of the page, making them understandable to both users and search engines.
Keyword Incorporation: While not to be stuffed, including primary keywords in the URL can be beneficial.
Consistency and Structure: URLs should be structured consistently site-wide. This includes the use of hyphens to separate words and the avoidance of unnecessary characters.
10. Internal Linking
Internal links connect one page of a website to another page on the same website:
Navigation: They aid in website navigation, helping users find relevant content.
Hierarchy and Structure: Internal links establish a hierarchy, allowing search engines to understand primary and secondary content.
Distribute Page Authority: They can help distribute “link juice” or authority throughout the site, potentially improving ranking for various pages.
11. External Linking
External links connect a page on your website to a page on a different website:
Authority and Credibility: Linking to reputable sources can enhance the credibility of your content.
Relevance: Ensure that external links are relevant to the context of your content.
Nofollow vs. Dofollow: Be aware of when to use “nofollow” attributes, especially for links that might be perceived as untrustworthy or paid.
12. Mobile Responsiveness
With an increasing number of users browsing the internet on mobile devices, having a mobile-responsive site is crucial:
User Experience: Ensures that users on mobile devices have an optimal viewing and interaction experience.
SEO Impact: Google and other search engines use mobile-friendliness as a ranking factor.
Adaptable Design: Content should adjust smoothly to various screen sizes, and interactive elements should be easily accessible.
13.Site Speed
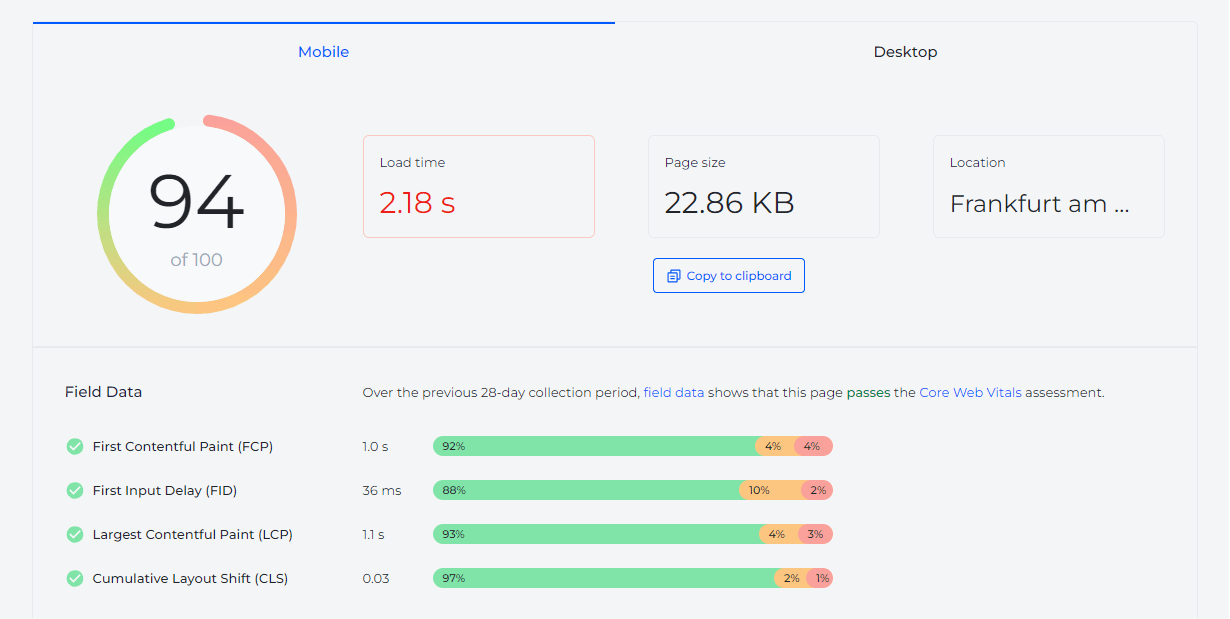
The time it takes for your web pages to load can significantly impact user experience and SEO:
User Engagement: Slow-loading pages can deter users, leading to increased bounce rates.
Search Engine Rankings: Site speed is a recognized ranking factor for search engines, especially on mobile.
Optimization Strategies: This includes compressing images, leveraging browser caching, reducing server response times, and using content delivery networks (CDNs).
On-Page SEO Checklist
Optimizing a webpage for search engines involves various steps, ensuring that both the content and the technical aspects of the page meet best practices for SEO. One of the fundamental elements to consider in this process is the URL structure.
1. Make sure your keyword is in your URL
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is essentially the web address of a particular page on your website. It not only serves as the location of your content but also provides both users and search engines with clues about the page’s content. Here’s why and how to ensure your target keyword is in your URL:
- Relevance and Context: When a URL contains the main keyword, it immediately gives users and search engines an idea about the page’s topic. This can enhance click-through rates from search results as users can quickly identify the relevance of the page to their query.
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing: While it’s beneficial to include your primary keyword in the URL, ensure it’s done naturally. Overloading the URL with multiple keywords can appear spammy and may negatively impact user perception and SEO.
- Simplicity and Brevity: Keep URLs concise and straightforward. Long URLs can be daunting or confusing, leading to reduced user trust. If your primary keyword is lengthy, consider using its most recognizable form.
- Consistency: Once you’ve set a URL with a particular structure and keyword, avoid changing it frequently. Regular URL changes can lead to broken links, and search engines might take time to re-index the new URL. If you must change a URL, ensure to set up proper 301 redirects from the old URL to the new one.
- URL Structure: If your website covers different topics or categories, use a structured URL approach, like “example.com/category/keyword”, to provide context.
- Dashes Over Underscores: In the SEO community, it’s generally recommended to use dashes (-) instead of underscores (_) to separate words in URLs. This makes them more readable and is recognized by search engines as word separators.
Incorporating the main keyword into the URL is just one of many steps in the on-page SEO checklist. However, it’s a vital one, as a well-structured URL provides a solid foundation for the overall SEO of a page.
2. Optimize your page title.
The page title is one of the most crucial SEO elements. It’s the first thing users see on search results and can greatly influence click-through rates.
Keyword Placement: Ideally, place your primary keyword towards the beginning of the title.
Length: Stay within 50-60 characters to ensure the title displays correctly in search results.
Relevance: Ensure the title accurately represents the content of the page.
3. Use headers.
Headers (H1, H2, H3, etc.) structure your content, making it more readable for users and understandable for search engines.
Hierarchy: Maintain a clear hierarchy. Start with an H1 for the main title, then H2 for subheadings, H3 for sub-subheadings, and so on.
Keyword Usage: Sprinkle relevant keywords across headers, but do so naturally.
4. Include keywords in your body copy.
The actual content of your page should be optimized for search while still being engaging for readers.
Density: Avoid keyword stuffing. Instead, aim for a natural flow.
Variety: Use synonyms and related terms to add depth and avoid redundancy.
5. Incorporate images, graphics, and other visuals.
Visuals enhance user engagement and can provide additional ranking opportunities.
Relevance: Ensure visuals align with and support the content.
Compression: Use compressed images to improve page load times without compromising quality.ц
6. Add a meta description.
While not a direct ranking factor, a compelling meta description can improve click-through rates.
Concise Summary: Describe the content of the page in under 160 characters.
Include Keywords: Incorporate your main keyword naturally.
7. Optimize visuals with alt-text.
Alt-text provides search engines with a description of visuals, making your site more accessible.
Descriptive: Clearly describe the image.
Keyword Usage: If applicable, include the primary keyword.
8. Add internal links.
Linking to other pages on your site can help distribute page authority and guide users to relevant content.
Relevance: Ensure links are relevant to the content and provide value to the reader.
Anchor Text: Use descriptive anchor text, avoiding generic terms like “click here.”
9. Add external links.
Linking out to authoritative sources can increase the credibility of your content.
Trustworthy Sources: Link to reputable, high-authority sites.
Nofollow vs. Dofollow: Understand when to use each type of link attribute.
10. Target Featured Snippets.
These are special search results that appear at the top of SERPs, providing quick answers.
Structured Data: Use schema markup to provide context to search engines.
Q&A Format: Answer common questions clearly and concisely.
11. Improve User Engagement.
Engaged users are more likely to convert, share, and return to your site.
Quality Content: Write engaging, valuable content that addresses user intent.
Interactive Elements: Incorporate elements like polls, quizzes, or interactive graphics.
How to Manage On-Page SEO at Scale
Managing on-page SEO for a single page can be straightforward, but when you’re looking at hundreds or thousands of pages, the challenge escalates. Here’s a structured approach to efficiently and effectively manage on-page SEO across a large website:
Download Now: On-Page SEO Template
Before diving in, make sure to download our comprehensive on-page SEO template. This tool will assist you in tracking, analyzing, and planning your on-page SEO strategy at scale.
1. Crawl your website.
Before making any changes, understand your website’s current state.
- Use SEO Tools: Tools like Screaming Frog or SEMrush can help you crawl your website to detect issues and understand the current structure.
2. Conduct an SEO audit and define your site architecture.
Identify issues and opportunities.
- Audit Key Elements: Check for broken links, missing meta descriptions, duplicate content, etc.
- Site Hierarchy: Ensure a logical and user-friendly site structure, which helps both users and search engines.
3. Update URLs, page titles, and meta descriptions.
Consistency is key.
- Standardize Formats: Use a consistent structure across all URLs and titles for better user experience and SEO.
4. Track keywords and topics for each page.
Know what each page aims to rank for.
- Keyword Mapping: Assign specific keywords to each page to avoid keyword cannibalization.
5. Establish value propositions for each page.
Determine the unique value each page offers to its audience.
- Unique Content: Avoid duplicate content and ensure each page serves a distinct purpose.
6. Define your target audience.
Know who you’re writing for.
- Personas: Develop detailed personas to understand your audience’s needs, questions, and pain points.
7. Plan new page titles.
Titles are the first impression.
- Keyword-Rich: Ensure primary keywords are present and titles are enticing to users.
8. Add new meta descriptions.
Craft compelling meta descriptions for higher click-through rates.
- Unique Descriptions: Ensure each page has a distinct meta description relevant to its content.
9. Review and edit page content as needed.
Regularly update your content to keep it fresh and relevant.
- Content Calendar: Schedule periodic reviews to update statistics, add new information, or improve readability.
10. Incorporate visual content.
Engage users with relevant images, videos, and infographics.
- Optimized Visuals: Ensure all visuals are optimized for speed and SEO.
11. Add relevant links.
Enhance the user experience and distribute page authority.
- Internal and External: Maintain a balance between linking to your content and referencing external authoritative sources.
12. Optimize for conversions.
Turn visitors into leads or customers.
- CTAs: Use clear and compelling calls-to-action.
- A/B Testing: Regularly test page elements to see what drives higher conversion rates.
Put Your On-Page SEO to Work
Now that you’ve equipped yourself with a comprehensive understanding of on-page SEO, it’s time to execute. Knowledge without action is like a car without fuel – stationary and unproductive.
Start Small: Begin with the pages that get the most traffic or are of strategic importance. Optimize these pages first for quick wins.
Iterate: On-page SEO isn’t a “set it and forget it” task. Continuously monitor your results, experiment with different strategies, and refine your approach based on performance data.
Feedback Loop: Regularly seek feedback from users and other stakeholders. Sometimes, the best insights come from those outside the SEO bubble.
Stay Updated: The world of SEO is ever-evolving. Keep yourself informed about the latest trends, algorithm updates, and best practices.
Integration: Integrate your on-page SEO efforts with other digital marketing strategies like content marketing, social media, and paid advertising for a holistic online presence.
Website SEO Checker & Audit Tool to Boost Your On-Page SEO
For those looking to optimize their website’s on-page SEO, the Site Audit tool by Sitechecker is a must-have. It delves deep into your website, thoroughly examining elements such as meta tags, headings, and keyword usage, ensuring that your on-page factors align perfectly with SEO best practices. This detailed analysis offers invaluable insights into how search engines view your content and where improvements can be made.
In addition to its robust on-page SEO analysis capabilities, the Site Audit tool brings an array of other essential features to the table. It checks for broken links, assesses page speed, evaluates mobile usability, and much more. The intuitive interface and actionable recommendations make it easy to identify and rectify any issues, ensuring your website is fully optimized and ready to rank higher in search results.
Leave No Page Unchecked!
Dive deep into your website with our comprehensive Website Audit tool.
Summary
On-page SEO plays a pivotal role in determining how well your website performs in search engine results. It involves optimizing various elements on your web pages, ensuring they are both user-friendly and search engine-friendly.
From understanding the basics like keyword placement in URLs and meta descriptions to advanced strategies like targeting featured snippets and optimizing for conversions, effective on-page SEO requires a well-rounded approach. As with any digital marketing endeavor, the key is consistency, regular monitoring, and a willingness to adapt and evolve.
Which is more necessary: on-page or off-page SEO for ranking?
What are SEO factors on-page & off-page?
What are the 5 important on-page SEO factors?
- High-quality, relevant content.
- Optimal keyword placement.
- Meta descriptions and title tags.
- Mobile-friendliness.
- Internal linking structure.