The x-default hreflang attribute is the tag used to tell the search engine that your website has a default or universal webpage. It tells search engines and browsers that they don’t need to redirect users to a webpage in the local language or that it’s intended for the local region. However, when this value is missing, it can create an issue, which is the missing x-default hreflang annotation.
For those who prefer learning the solution via video, here is a video link to help you fix the missing x-default hreflang annotation issue:
You can also use this guide to learn about using x-default hreflang for international landing pages.
What Does “X-Default Hreflang Annotation Empty” Mean?
As you know, the hreflang annotation lets browsers and search engines know if a version of your website is available in a specific language for users in a certain region/language. In other words, it’s for specific audiences. What about more general audiences? How should you code your website to read to search engines and browsers?
Here is where the x-default hreflang annotation comes in. It is a tag that tells the web browser or search engine that you don’t have a website version in a certain language or for a certain region.
However, you may encounter the error that says, “x-default hreflang annotation is missing.” It means the search engine can’t choose a language to display the website in.
What Triggers This Issue?
This issue comes up when your URLs have no x-default hreflang annotation.
How to Check the Issue
Do a check on your website’s coding. You can tell that you’ve got a problem with the x-default hreflang tag when it gives you the report about the missing annotation.
Sitechecker can significantly improve your website’s global SEO strategy by addressing “Missing hreflang annotations.” The screenshot you’re viewing shows a common issue many multilingual websites face, which can negatively impact your international SEO efforts.
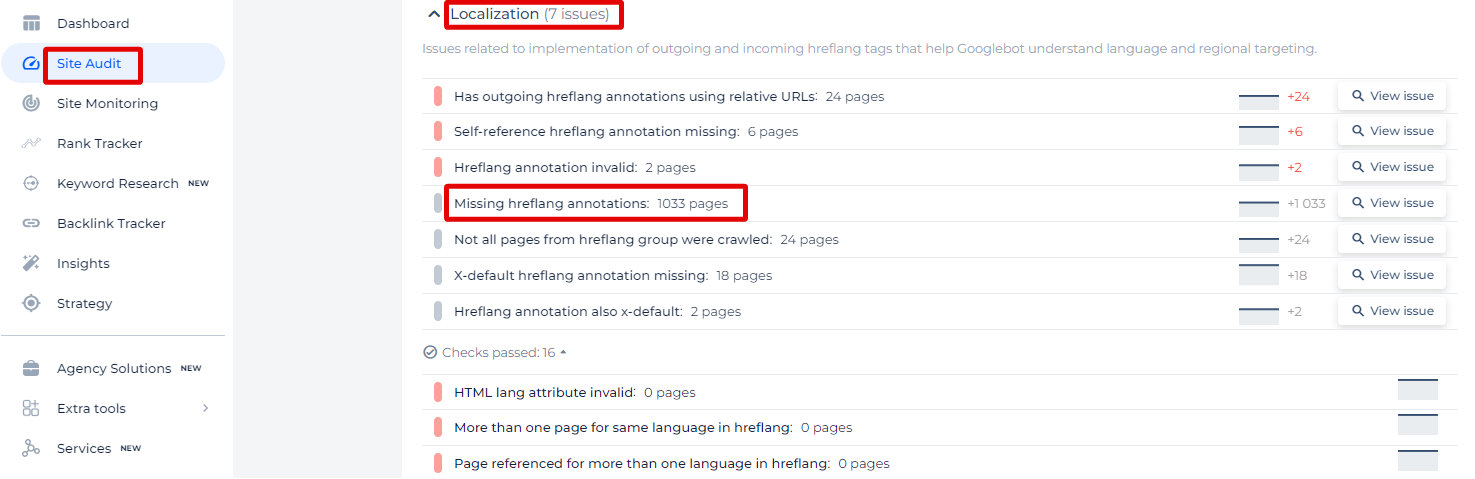
This section specifically focuses on the ‘Localization’ category, indicating that there are 1,033 pages on your website that lack the necessary hreflang annotations. These annotations are crucial because they inform Google about the language and geographical targeting of your webpages, which helps the search engine serve the correct version of your content to users based on their location and language preferences.
By clicking on ‘View issue’, Sitechecker will not only provide you with a comprehensive list of the affected pages but also offer insights into the dynamic of the issue over time.
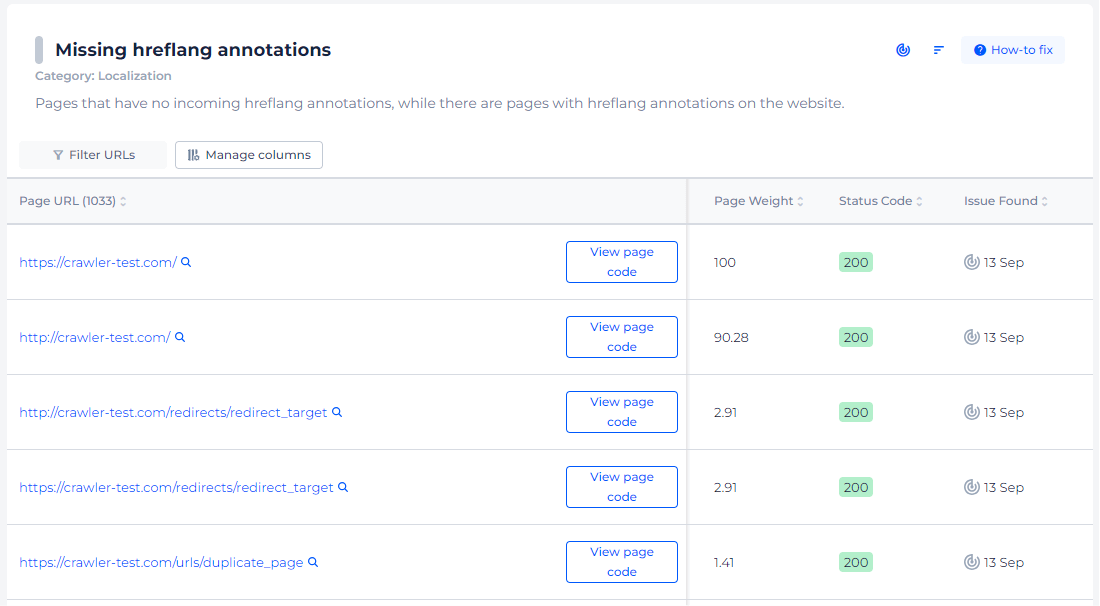
Upon selecting the “View page code” option for any URL listed, the tool will not only show you the exact pages missing the hreflang annotations but also provide additional critical information. This includes the page weight, which helps gauge the size of the page content, and the status code, which confirms whether the page is successfully accessible or not. The ‘Issue Found’ date gives a timeline, which is valuable for tracking when the issue was first detected.
Expand Your Global Presence!
Use our Hreflang Checker to identify missing annotations and tailor your content for users worldwide.
Why Is This Important?
Always make sure you have an x-default hreflang attribute for your website. This is the language in which search engines will display your website if you don’t have a version reciprocal to the local area or language. Otherwise, the language barrier and conflicts can affect user experience.
Most websites use the link to English versions of their websites as the default link since English is widely spoken throughout the globe.
Steps to Fix the X-Default Hreflang Annotation Empty Issue
1. Identify the Problematic Pages
Use tools like Google Search Console or Sitechecker to find pages with empty or incorrect x-default annotations.
2. Add or Correct the X-Default Hreflang Tag
Edit the HTML of the problematic pages to include a correct x-default language attribute tag.
The x-default language attribute tag should point to the most generic version of your page, typically the homepage or a page that serves as a fallback for all users.
3. Example of Correct Hreflang Implementation
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://www.example.com/en/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es" href="https://www.example.com/es/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="fr" href="https://www.example.com/fr/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="https://www.example.com/" />
4. Ensure Consistency Across Pages
Make sure that the x-default hreflang annotation is consistent across all pages of your website that use language attribute tags.
5. Validate Your Changes
Use the Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool to check if Google correctly processes the updated language attribute tags.
You can also use online tools like the Hreflang Tag Checker to validate your implementation.
6. Update the Sitemap (if necessary)
If you are using an XML sitemap to list language attribute tags, ensure that it is updated with the correct x-default annotations.
Example:
<loc>https://www.example.com/en/</loc>
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://www.example.com/en/"/>
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="es" href="https://www.example.com/es/"/>
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="fr" href="https://www.example.com/fr/"/>
<xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="https://www.example.com/"/>
</url>
7. Monitor and Review
Regularly monitor your website to ensure the hreflang annotations are working as expected.
Keep an eye on Google Search Console for any new issues related to hreflang tags.
Following these steps, you can fix the x-default language attribute annotation empty issue, ensuring that search engines understand your website’s internationalization correctly.
Final Idea
The x-default language attribute informs search engines that a default or universal webpage is available when no specific language or region is detected. Missing this tag can cause issues, as search engines can’t determine the correct language to display. To fix this, check your site’s coding and ensure every page has the x-default hreflang attribute, typically pointing to an English version or a general page. Tools like Sitechecker can help identify and resolve missing language attribute annotations, improving your website’s international SEO strategy.