The hreflang attribute is one of the most complex tools for website promotion. It is used for portals that have several versions of the same content in different languages. In fact, hreflang is a code that marks different URLs of the site with similar content in a different language(s) or in the same language but for different regions.
What no Reciprocal Hreflang Means
When testing a website, the following error often occurs: there is no reciprocal hreflang, namely, there is no return tag, and on some pages, there are no links of this attribute to other pages. In other words, the hreflang link on page P leads to page M, but page M should also have a link to return to page P.
Why is This Important?
The absence of a return tag can disrupt the correct operation of search engines, which will ignore this code.
What Triggers This Issue
Typically, the main cause of the error for the hreflang attribute is typos in the code or URL. This results in incorrect attributes that are considered wrong by search engines. Such attributes are not indexed by search engine crawlers and, therefore, not implemented.
Common Errors in the Hreflang Code
Let us review common mistakes made when writing the hreflang code:
- Incorrect sequence of attribute components. You should always use the language code first before the country code. You should follow the standards: language – ISO 639-1, local – ISO 3166-1 alpha-2. For the attribute to be configured correctly, it is important to specify the language of the page; the country can be omitted. But not vice versa: if you specify the region but forget the language, the attribute will not work correctly. More details can be found here: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/advanced/crawling/localized-versions .
- Inaccurate use of the separation line between language and region codes. You cannot use an underscore or a dash. Only a hyphen is allowed.
- Inconsistencies in the hreflang setting. Proper attribute writing implies that one language matches one page.
- The inaccurate spelling of letters or numbers in the code. To avoid such errors, use the hreflang tag generator tool.
- Errors in links. Several scenarios are possible here:
- redirect to non-existent pages – 4xx (5xx) errors;
- absence of some hreflang element, for example, language is not indicated;
- redirect to another page – in this case, the other address is not added to the search engine database;
- use of relative links with the first part missing;
- absence of reciprocal links confirming the attribute action.
All of the above errors lead to the outcome that the page will be ignored by search engines.
How to Check the Issue
In the Localization category, our Sitechecker tool has identified a specific issue called ‘Missing reciprocal hreflang (no return-tag).’ This means that while some pages on your website signal to Googlebot that there are equivalent versions in other languages or regions, there’s no confirmation back from those linked pages. In other words, there’s a missing handshake that tells search engines these pages are related.
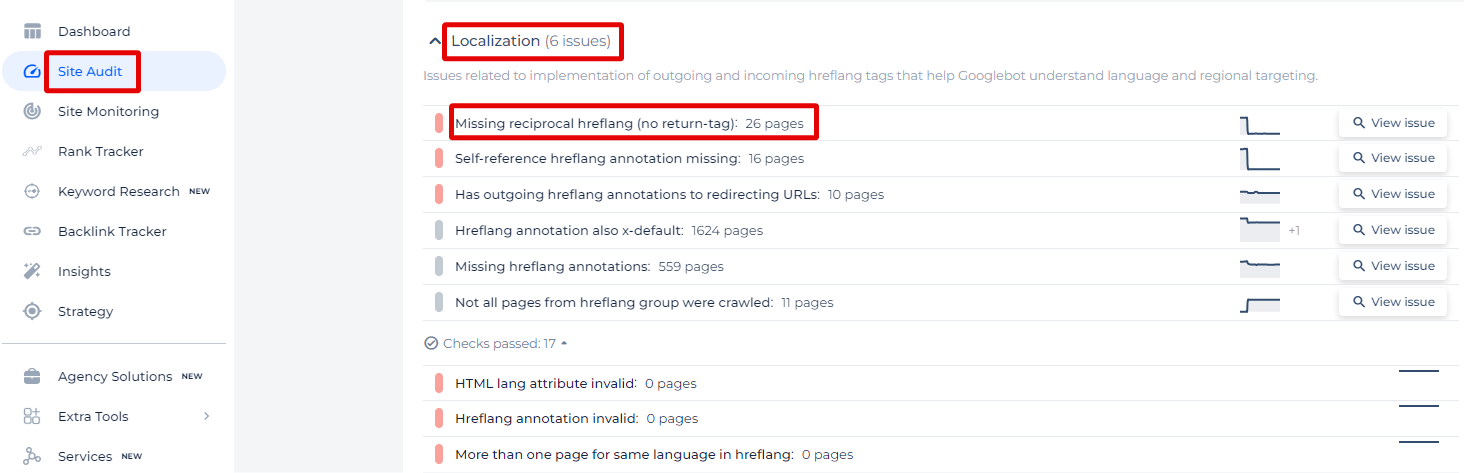
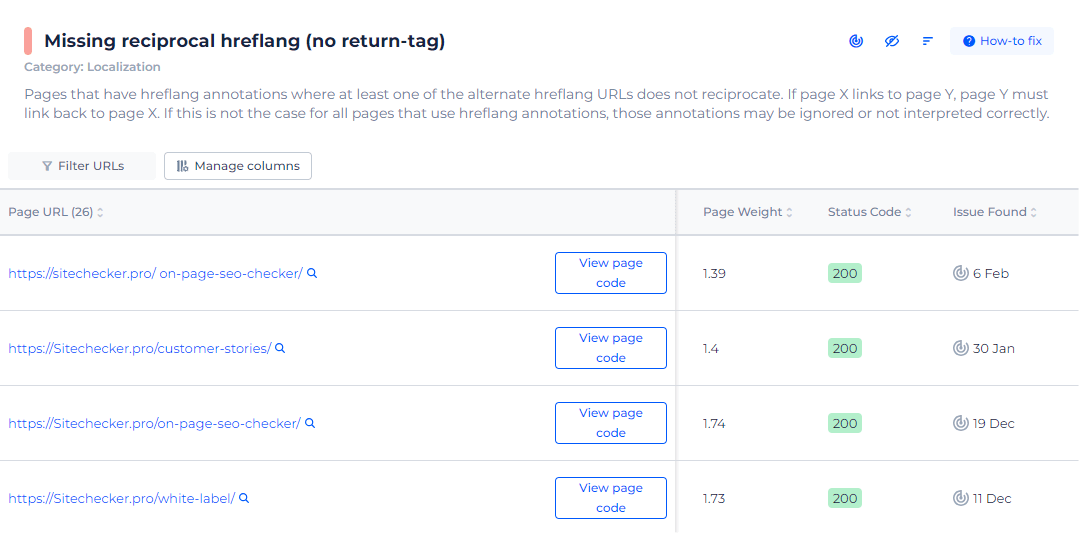
By selecting ‘View issue,’ you can see exactly which pages need this vital bidirectional link, ensuring your international SEO is as effective as possible. We don’t just give you a page count; we provide actionable insights. You’ll see a clear list of the affected URLs along with details like page weight and status codes, helping you prioritize your fixes based on the impact each page has on your site’s SEO performance.
Fix Missing Reciprocal hreflang Tags!
Use our hreflang checker to identify missing reciprocal links and enhance global SEO performance.
How to Fix the Issue?
Fixing the “Missing reciprocal hreflang (no return-tag)” issue involves ensuring that each hreflang attribute in your website’s HTML is reciprocated with a corresponding return link. This ensures that search engines understand the relationship between the different language versions of your pages. Here’s how you can address this:
1. Identify the Pages with Language targeting Tags
Locate the pages on your site that use the language attribute. This is usually in the <head> section of your HTML and looks like this:
<link rel="alternate" href="http://example.com/en/" hreflang="en" />
2. Ensure Reciprocal Links
For each page that references an alternate language version, make sure the referenced page also references back. For instance, if example.com/en/ references example.com/fr/, then example.com/fr/ should also reference example.com/en/.
3. Update Your HTML
Edit the HTML of each page to include the appropriate language attribute tags with reciprocal links. Here’s an example setup for two pages, one in English and one in French:
English Page (example.com/en/):
<link rel="alternate" href="http://example.com/en/" hreflang="en" />
<link rel="alternate" href="http://example.com/fr/" hreflang="fr" />
French Page (example.com/fr/):
<link rel="alternate" href="http://example.com/fr/" hreflang="fr" />
<link rel="alternate" href="http://example.com/en/" hreflang="en" />
- Verify the Implementation. After updating the HTML, use tools like Google Search Console and Hreflang Checker to check for any language attribute errors. You can also use online validators like hreflang.org to ensure that your language attribute tags are correctly implemented and reciprocal.
- Automate the Process (Optional). If your site has a large number of pages, consider automating the hreflang tag generation and insertion process. Many content CMS and e-commerce platforms have plugins or extensions that can help manage hreflang tags efficiently.
- Regular Audits. Periodically audit your language targeting tags to ensure they remain correct, especially if you frequently add new content or languages to your site.
By ensuring that each language attribute tag on your pages is reciprocated, you help search engines accurately index and serve the appropriate language version of your content to users, improving your international SEO.