A “400 Bad Request” error is an HTTP status code that indicates the request sent by the client (such as a browser or a web scraper) to the server cannot be processed. This is often because the request was malformed in some way, making it impossible for the server to understand or fulfill.
A 400 Bad Request error in an SEO context typically means that a search engine bot, like Google’s Googlebot, is having trouble crawling a URL on your website. When search engine bots cannot successfully crawl a URL, it can lead to issues with indexing that page, which may affect your website’s search engine rankings.
400 Bad Request Error Impact on SEO
A 400 Bad Request error can significantly affect various aspects of a website’s SEO, impacting everything from user experience to site indexing and visibility on SERPs.
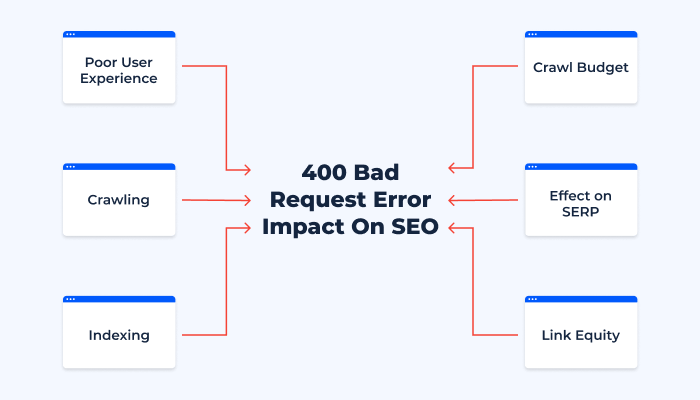
User experience is a critical factor in SEO, with search engines like Google emphasizing delivering high-quality and relevant results to users. When a user encounters a 400 error, it results in a poor user experience, leading to high bounce rates. Over time, high bounce rates can signal to search engines that your website may not be providing valuable content or a good user experience, negatively impacting your website’s ranking in search results.
In the context of website crawling and indexing, persistent 400 errors can create significant obstacles. Search engine bots or crawlers rely on the ability to access and read website content to understand what a site is about. Encountering a 400 error means the crawler has hit a page it cannot access due to issues like incorrect URLs or server configuration problems. This impediment directly affects the next step – indexing.
Indexing involves search engine bots taking the data gathered during crawling back to the search engine to build an index. Search engine algorithms then use this index to determine where and how to rank your site in the SERPs. However, if bots encounter 400 errors during the crawling process, they cannot access the content on those pages, which means those pages won’t be indexed. Consequently, your website has less content to rank with, potentially reducing its visibility on SERPs.
Another issue is the ‘Crawl Budget’. Search engine bots have a limit to the number of pages they will crawl on your site within a specific timeframe. When a substantial portion of this budget is wasted on pages returning 400 errors, it means less of your site is being crawled and indexed within that timeframe.
This inefficient use of crawl budget could delay updating your website’s status in the search index.
Furthermore, persistent 400 errors could lead to a drop in your organic search traffic. If many pages on your site are returning 400 errors and hence not being indexed, it reduces the amount of content that you have ranking on SERPs. Additionally, if other sites are linking to a page on your website that’s now returning a 400 error, this situation not only wastes potential referral traffic but also the ‘link equity’ those backlinks could be passing on.
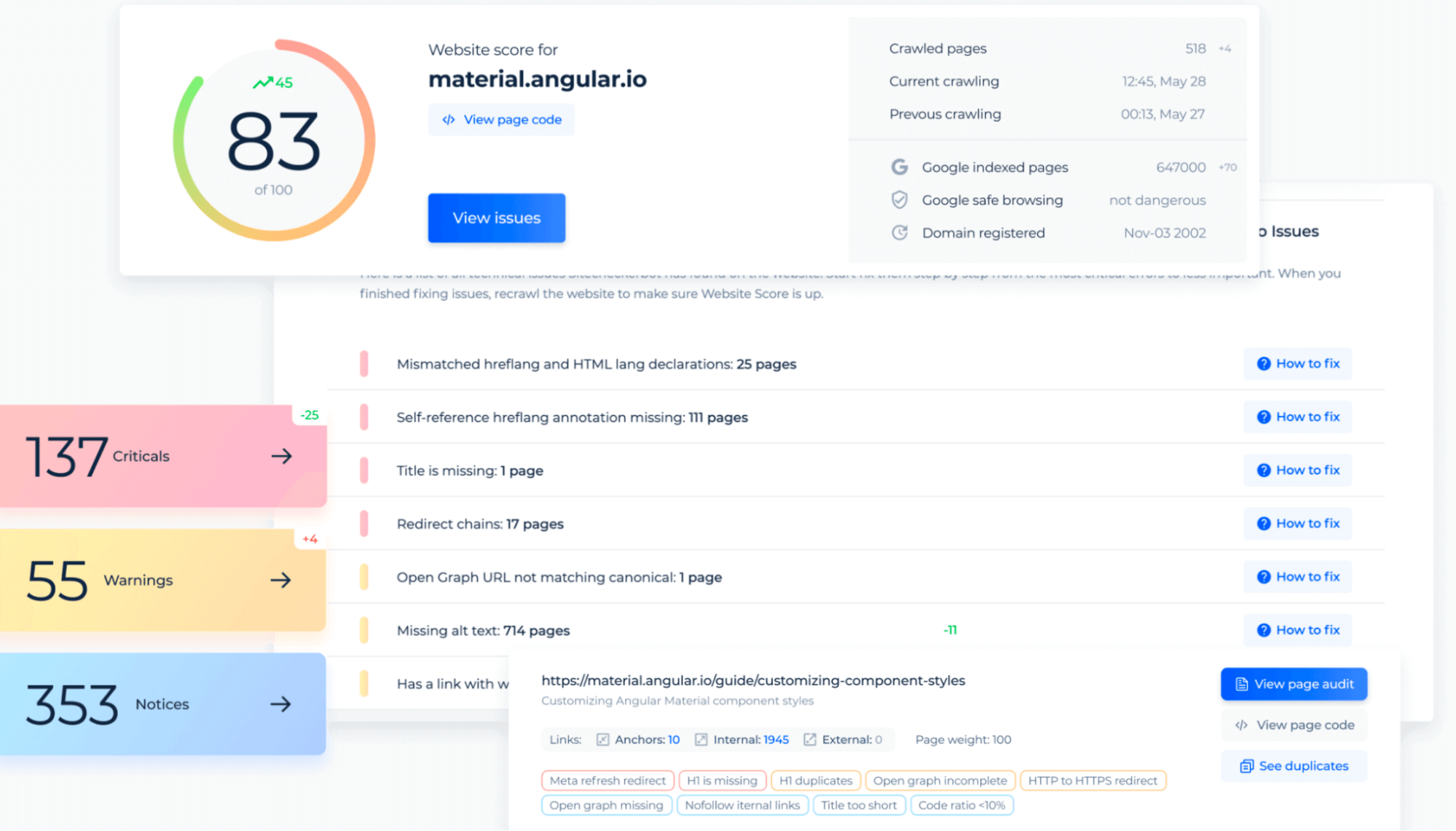
Overall, it’s essential to regularly monitor and fix 400 errors in your SEO strategy. Tools like Real-Time Cloud-Based Website Crawler can help identify these errors and provide information to rectify them.
Also, if a page has been removed permanently, it’s important to implement a 301 redirect to a relevant page, preserving both user experience and link equity.
Common Causes of 400 Errors
A 400 Bad Request error indicates that the server was unable to understand a request due to invalid syntax. Several factors can lead to a 400 error.
Let’s delve into some of the most common scenarios:
| Incorrect URL Structure | One of the most frequent causes of a 400 error is an incorrectly structured URL. If a URL is typed incorrectly or structured in a way that the server does not understand, it can result in a 400 error. This situation can occur when there are incorrect characters or if a user manually types a URL and it’s misspelled or formatted incorrectly. |
| Invalid or Expired Cookies | When a user’s browser sends information to the server in a cookie that the server does not understand or has expired, a 400 error may occur. Clearing your cookies is one way to resolve this issue. |
| Server Issues | If the server is not properly configured to understand and respond to requests from a client’s browser, it can return a 400 error. This issue might be due to a problem in the server’s software or its configuration. |
| Malfunctioning Scripts | In some cases, client-side scripts that manipulate HTTP requests can lead to a 400 error. This situation can occur if the script modifies the request in a way that the server can’t understand. |
| File Size Too Large | When the request sent to the server is too large, a 400 error might occur. This could happen, for instance, when a user tries to upload a file that is larger than the server is configured to handle. |
| Invalid Headers | HTTP headers let the client and the server pass additional information with an HTTP request or response. If these headers are configured incorrectly or include invalid information, it could lead to a 400 error. |
| Corrupted Browser Cache | If the cached version of the page in the user’s browser is corrupted or out of date, it can result in a 400 error. In such cases, refreshing the page or clearing the browser cache can resolve the issue. |
Remember, the key to resolving 400 errors is identifying the cause. Tools like Google Search Console, website server logs, and other website monitoring tools can be used to detect these issues and their sources.
Once the cause is identified, steps can be taken to rectify the issue, enhancing the user experience and ensuring that your site remains SEO-friendly.
How to Fix a 400 Bad Request Error From an SEO Perspective
1. Verify The URLs
Check your server logs or use a tool like Google Search Console to identify the URLs that are returning a 400 error. Make sure these URLs are correctly formatted and don’t contain illegal characters or spaces.
2. Test Robots.txt
Your website’s robots.txt file gives directions to search engine crawlers about which pages to crawl or not crawl. If there’s something wrong in your robots.txt file, it could cause crawling issues. Make sure this file is correctly set up and does not unintentionally block important pages on your website.
3. Fix Broken Links
If your website links to a page that returns a 400 error, it can harm your SEO. Make sure all internal and external links on your website lead to valid pages. Use a broken link checker tool to find and fix any broken links.
4. Check Redirections
If you’ve recently migrated your website or changed URLs, it’s possible that the redirections are not set up correctly, which can result in 400 errors. Use a tool like URL Redirect Checker to identify any redirection errors and correct them.
5. Update Your XML Sitemap
Your XML sitemap helps search engine bots find and crawl all of the important pages on your website. If your sitemap includes URLs that return a 400 error, it can cause problems. Make sure your XML sitemap only includes valid URLs.
You can use the free XML Sitemap Checker to detect any problems.
6. Use a Crawl Simulator
Use a tool like the Google Search Console URL Inspection Tool or a website crawler like Website Crawler for Technical SEO Analyze to simulate how a search engine bot would crawl your website. These tools can help you identify any craw l errors.
Also, see a video by Kinsta about reasons and recommendations on how to fix 400 Bad Request error:
Remember that it’s essential to fix 400 errors as soon as possible, as they can impact your website’s search engine rankings. After making the necessary changes, you should submit your updated sitemap to Google Search Console to ensure Google’s search engine bots can successfully crawl all of the pages on your website.
HTTP Status Code Checker for Detecting 400 Errors
The HTTP Status Code Checker by Sitechecker.pro is an essential tool for webmasters and SEO experts. It scans your website and provides a detailed report of all HTTP status codes, making it easier to identify and resolve issues, including 400 Bad Request errors.
Simply enter your website URL, and the tool will find and display the corresponding HTTP status codes for each page. It shows the URL of the page, the found HTTP status code, and the type of HTTP response.
For 400 errors, this tool helps pinpoint the exact location of the problem, aiding in quick diagnosis and resolution. Besides, it identifies other status codes such as 301 and 302 redirects, 404 Not Found errors, 500 Internal Server Errors, etc.
In summary, Sitechecker.pro’s HTTP Status Code Checker is a powerful resource for maintaining a healthy and SEO-friendly website, as it simplifies detecting and resolving HTTP status code issues.
Conclusion
“400 Bad Request” error signifies a request a server can’t process, usually due to malformed syntax. In SEO terms, this error can disrupt the crawling and indexing of your website by search engines, impacting your site’s rankings.
The error can degrade the user experience, affect the visibility of your site on SERPs, and reduce organic search traffic. Common causes range from incorrect URL structures and server issues to invalid headers and corrupted browser caches.
Identifying and rectifying these errors is crucial for maintaining a healthy, user-friendly, and SEO-optimized website. Utilizing tools like Sitechecker.pro’s HTTP Status Code Checker can be beneficial in spotting and troubleshooting these issues.