What is Google’s Knowledge Graph?
The Google Knowledge Graph is an innovative system introduced by Google to enhance its search engine’s results with information gathered from a variety of sources. It is designed to provide users with a quick and concise answer to their queries directly in the search results, often without the need for users to click on a search result link. But how does it achieve this?
At its core, the Knowledge Graph is a vast database of facts about people, places, events, and things, and the relationships between them. It’s not just a collection of data, but rather a structured understanding of real-world entities and how they interact. This means when you search for a famous person, a historic event, or even a popular movie, the Knowledge Graph can provide a summarized box of information, commonly known as the “Knowledge Panel,” on the search results page.
Here’s a quick introduction to what a Knowledge Graph is:
Here’s what makes the Knowledge Graph unique:
– Entity Recognition: Instead of relying solely on keywords, the Knowledge Graph understands entities. For example, when you search for “Eiffel Tower,” it knows you’re referring to the iconic structure in Paris and not just the words “Eiffel” and “Tower.”
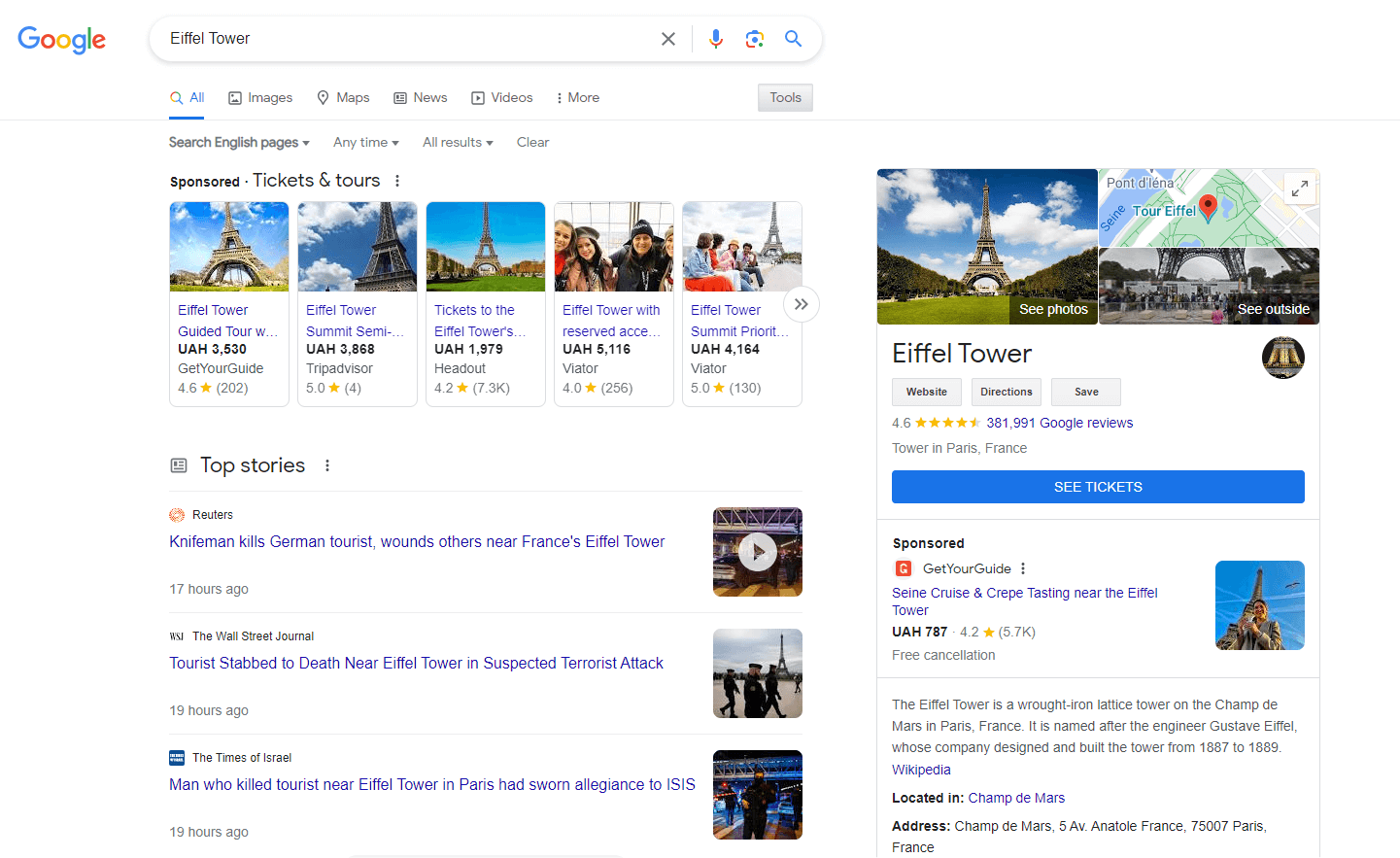
– Rich Information: The Knowledge Graph provides a wealth of information in one place. For a famous personality, you might see their date of birth, notable works, and related people. For a movie, you might get the cast, release date, and a brief synopsis.
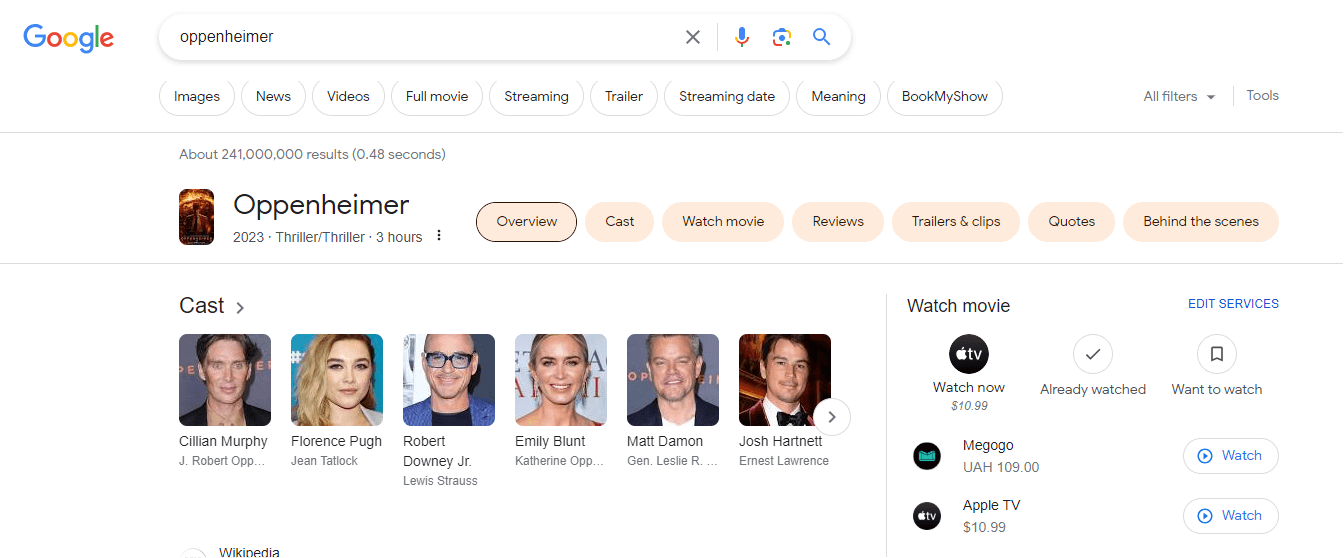
– Semantic Understanding: The Knowledge Graph understands the context. For instance, if you search for “apple,” it will try to determine whether you’re searching for the fruit or the tech company based on the context of your query.
– Direct Answers: For many queries, Google provides direct answers. For example, asking “When was the Declaration of Independence signed?” might yield a direct date answer, courtesy of the Knowledge Graph.
The introduction of the Knowledge Graph marked a significant shift in online search, moving from keyword-based searches to an entity-based model. This change aimed to make search results more relevant, accurate, and user-friendly, providing a richer search experience for users worldwide.
An Important Note on Disambiguation
Disambiguation is a crucial concept when it comes to understanding the workings of Google’s Knowledge Graph. At its core, disambiguation refers to the process of resolving ambiguities in search queries to ensure that the information presented to the user is relevant and accurate. With countless words and phrases in the English language (and other languages) having multiple meanings, disambiguation becomes an essential task for search engines.
Let’s delve into why disambiguation is important for the Knowledge Graph:
| Multiple Meanings | A single term can have various meanings based on its context. For instance, the word “bat” could refer to the flying mammal, a piece of sports equipment, or even an action (to bat one’s eyes). Without proper disambiguation, search results could be misleading or irrelevant. |
| User Intent | The Knowledge Graph aims to understand the user’s intent behind a search query. Disambiguation helps in this by analyzing the context of the search and other related terms to deduce what the user is likely looking for. For example, if someone searches for “jaguar speed,” the intent is probably about the animal’s speed, not the car brand. |
| Entity Differentiation | In the world of the Knowledge Graph, entities are distinct items or concepts. Disambiguation ensures that entities with similar or identical names are correctly identified and differentiated. For instance, “George Washington” the historical figure needs to be distinguished from any other individual with the same name. |
| Improved User Experience | Proper disambiguation ensures that users receive precise and relevant information quickly, without having to sift through unrelated or incorrect data. This enhances the overall user experience and trust in the search engine. |
However, it’s worth noting that disambiguation isn’t always perfect. There are instances where the Knowledge Graph might misinterpret a user’s intent or provide information on a slightly off-topic entity. In such cases, Google relies on user feedback and continuous learning to refine and improve its disambiguation processes.
In conclusion, disambiguation is an integral part of the Knowledge Graph’s efforts to provide accurate and relevant information to users. By understanding and resolving ambiguities in search queries, the Knowledge Graph ensures that users receive the most appropriate information for their searches.
Entity Topic Types
Within the realm of Google’s Knowledge Graph, entities are at the heart of its functioning. These entities represent real-world objects, concepts, places, people, and more. They’re not just mere words or phrases but have attributes, properties, and relationships that provide a deeper understanding of the world. But what types of entities does the Knowledge Graph recognize? Let’s explore the primary entity topic types.
1. People: This encompasses individuals from all walks of life. From historical figures like “Albert Einstein” to celebrities like “Beyoncé,” the Knowledge Graph holds information about their life, achievements, relationships, and more.

2. Places: Geographical entities fall into this category. It could be countries like “Australia,” cities like “Tokyo,” landmarks like “The Grand Canyon,” or even specific locations like “The Louvre Museum.”
3. Things: This is a broad category that includes objects (e.g., “smartphone”), animals (e.g., “African elephant”), plants (e.g., “rose”), and other tangible items.
4. Concepts: Abstract ideas and theories fall into this category. Examples include “democracy,” “quantum physics,” or “impressionism.” These entities may not have a physical presence but hold significant importance in human understanding.
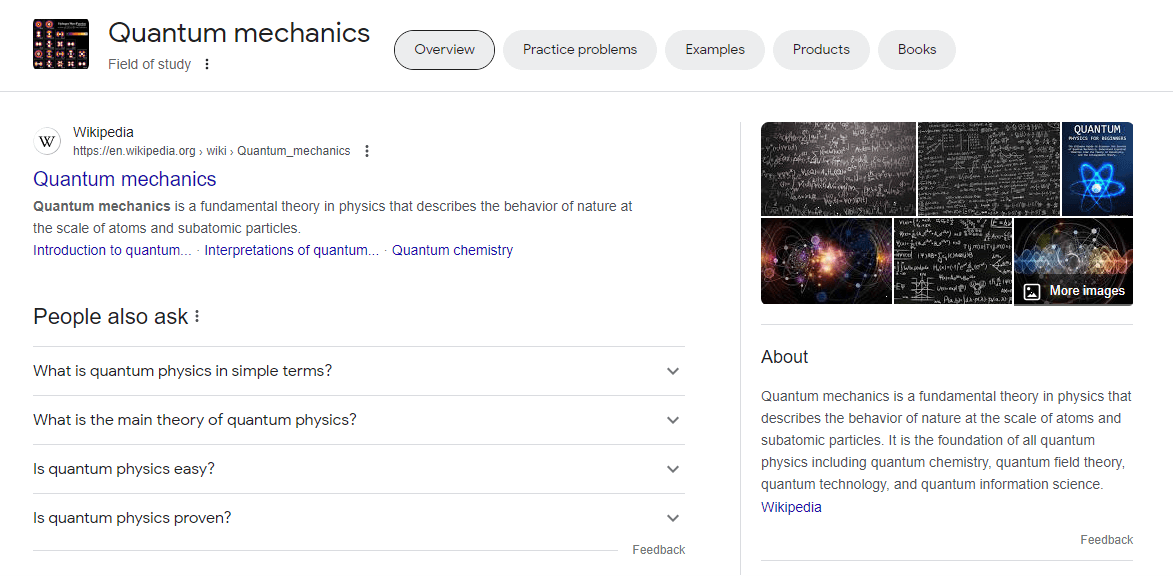
5. Events: Significant occurrences, whether historical like “World War II,” cultural like “The Oscars,” or recurring like “Thanksgiving,” are cataloged as entities.
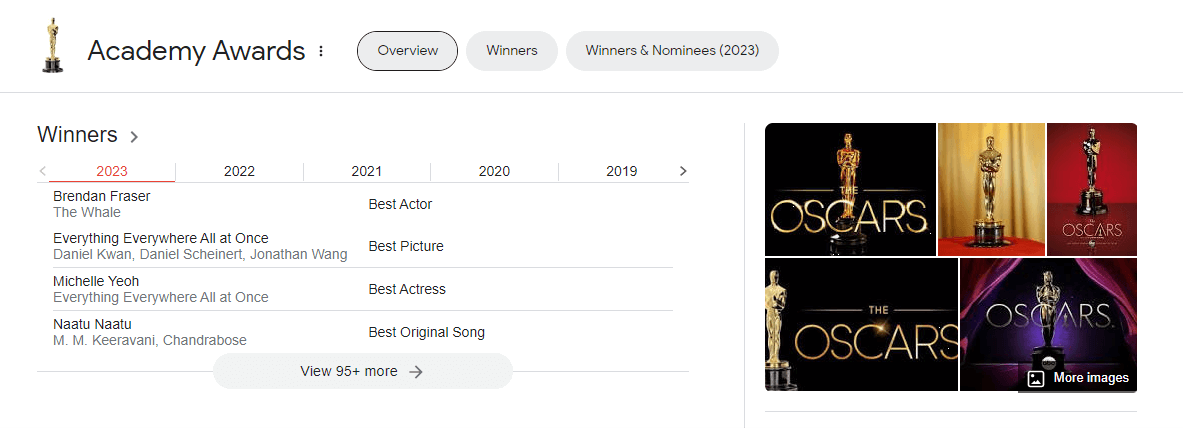
6. Organizations: Institutions, companies, NGOs, sports teams, and other group entities are recognized. For instance, “United Nations,” “Apple Inc.,” or “The New York Yankees.”
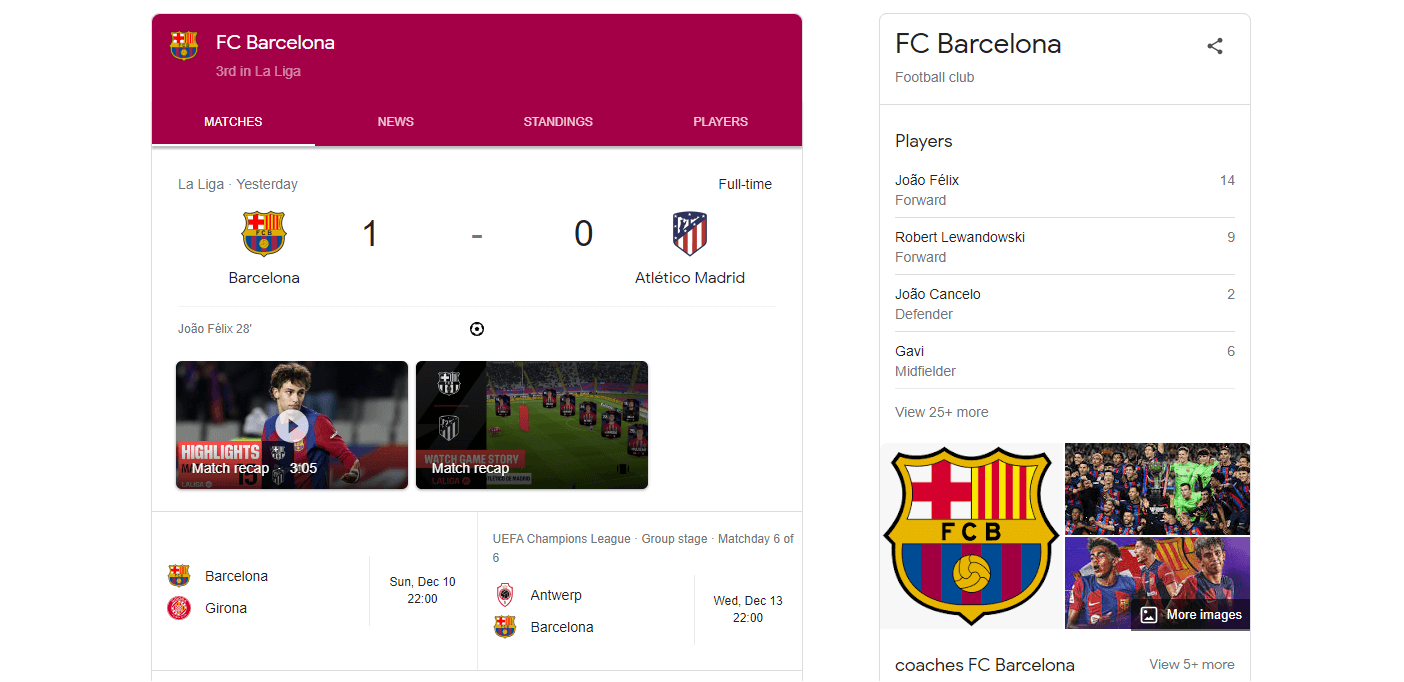
7. Art & Media: This category includes books (e.g., “Pride and Prejudice”), movies (e.g., “Inception”), music albums (e.g., “Thriller”), paintings (e.g., “The Starry Night”), and more.
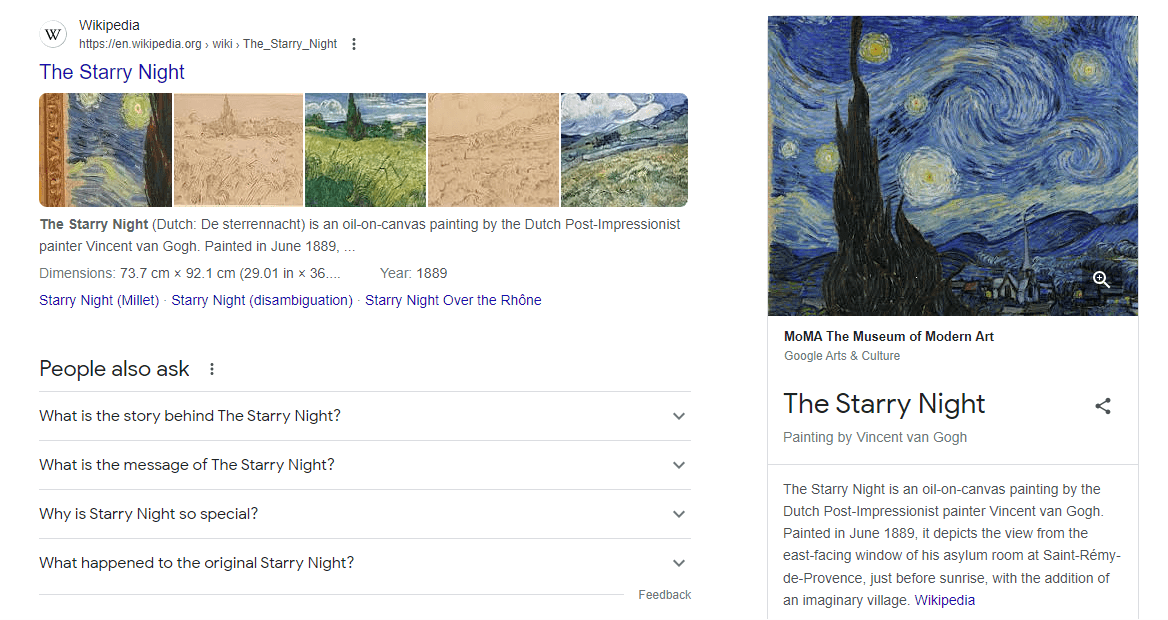
8. Dates & Time: Specific points in time, periods, or significant dates such as “Renaissance,” “21st Century,” or “July 4th, 1776.”
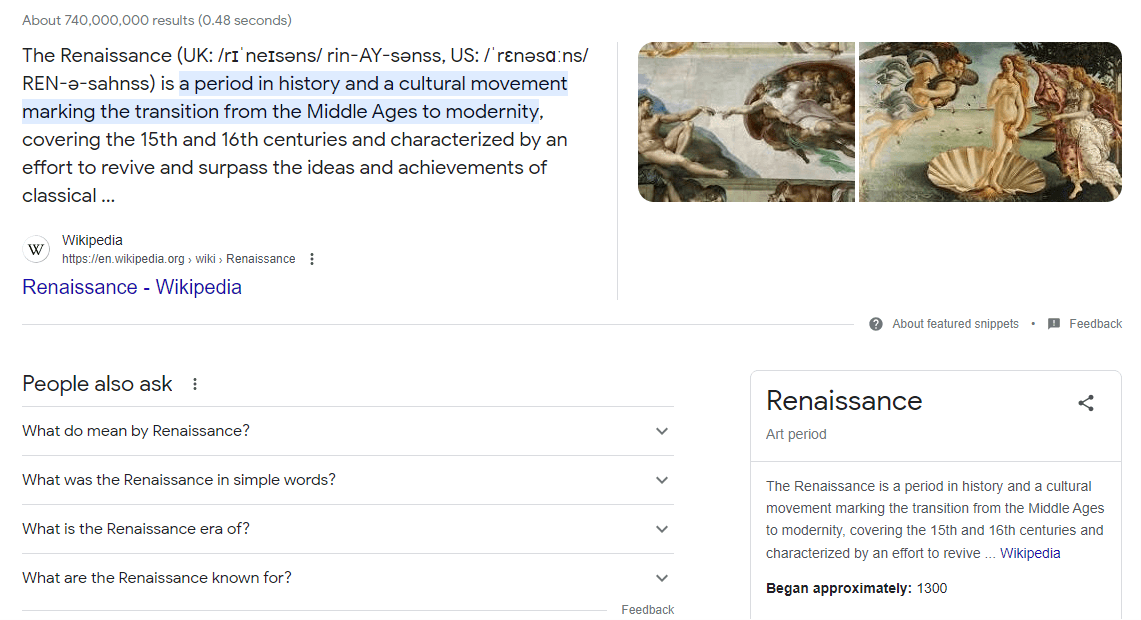
Understanding these entity topic types is essential because the Knowledge Graph doesn’t merely rely on keywords. It aims to understand the underlying entity a user might be referring to, ensuring more accurate and contextually relevant results. By categorizing information into these distinct entity types, the Knowledge Graph can form connections, draw insights, and provide users with a holistic view of their search topic.
In essence, entity topic types form the backbone of the Knowledge Graph’s understanding, allowing it to serve information that is not just factual but also interrelated and contextual.
How Does Google’s Knowledge Graph Work?
The Google Knowledge Graph is a marvel of modern technology, offering users quick and concise answers to their queries directly on the search results page. But the intricate mechanisms behind this feature are both vast and complex. Let’s delve into how the Knowledge Graph functions.
| Data Collection and Aggregation | The first step involves gathering vast amounts of data from various sources, including Wikipedia, CIA World Factbook, and other reputable databases. This data forms the foundation of the Knowledge Graph. |
| Entity Recognition and Categorization | Google’s algorithms identify and categorize the collected data into specific entities, as discussed earlier (e.g., people, places, events). This step ensures that each piece of information is tagged and organized appropriately. |
| Semantic Search and Understanding | Instead of solely focusing on keywords, the Knowledge Graph understands the context and meaning behind queries. This semantic understanding allows Google to determine user intent and provide the most relevant information. |
| Establishing Relationships | The Knowledge Graph doesn’t just store isolated facts. It identifies relationships between entities, helping to create a web of interconnected information. For example, it understands that Paris is the capital of France and that the Eiffel Tower is a landmark in Paris. |
| Continuous Learning and Refinement | Machine learning plays a significant role in the Knowledge Graph’s evolution. Based on user interactions, feedback, and new information, the system continuously refines its data and relationships to improve accuracy and relevance. |
| Displaying Knowledge Panels | When users search for an entity recognized by the Knowledge Graph, a summarized box of information, called a “Knowledge Panel,” may appear on the search results page. This panel provides a snapshot of essential details about the entity, sourced from the Knowledge Graph. |
| User Feedback Loop | Google allows users to provide feedback on Knowledge Panels. This feedback mechanism helps identify errors or inaccuracies, which are then used to refine the Knowledge Graph further. |
| Integration with Other Google Services | The Knowledge Graph isn’t limited to just search. It’s integrated with other Google services, such as Google Maps (for location-based entities) or Google Images (for visual representations), providing a holistic user experience. |
In essence, the Google Knowledge Graph is a dynamic system, continually evolving and adapting. Its primary goal is to understand the vast and intricate web of real-world information, distill it into structured data, and present it to users in a way that is both meaningful and useful. By bridging the gap between vast amounts of data and user queries, the Knowledge Graph ensures that search results are not just accurate but also contextually rich and relevant.
Knowledge Graph vs. Knowledge Panel
The terms “Knowledge Graph” and “Knowledge Panel” are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct components within Google’s search ecosystem. Understanding the difference between the two is crucial for anyone keen on grasping the nuances of Google’s search functionalities. Let’s break down these concepts:
Knowledge Graph:
- Definition: The Knowledge Graph is a vast, structured database developed by Google to enhance its search results. It comprises facts, information, and the relationships between different entities.
- Purpose: Its primary aim is to understand user queries in a more human-like manner, moving beyond simple keyword matching to provide contextually relevant search results.
- Scope: The Knowledge Graph encompasses a broad spectrum of information, covering countless topics, entities, and their interrelations. It’s a behind-the-scenes mechanism that powers many of Google’s advanced search features.
- Data Sources: Information within the Knowledge Graph is aggregated from reputable sources, including Wikipedia, public databases, licensed data, and more.
Knowledge Panel:
- Definition: The Knowledge Panel is a visual representation of specific information sourced from the Knowledge Graph. It appears on the search results page, typically to the right of the search results on desktop or at the top on mobile devices.
- Purpose: Its main goal is to provide users with a concise, summarized overview of a topic or entity, offering key details without the need to click through to another website.
- Scope: A Knowledge Panel focuses on a specific entity or topic. For instance, a search for “Mona Lisa” might display a Knowledge Panel with details about the painting, its history, and its artist.
- User Interaction: Users can interact with Knowledge Panels, exploring related topics, viewing images, and even providing feedback if they find inaccuracies.
In summary, while the Knowledge Graph is a vast, interconnected database that understands and maps the relationships between different pieces of information, the Knowledge Panel is a user-facing feature that presents selected pieces of that information in a concise and visual manner on the search results page. One can think of the Knowledge Graph as the vast library of information, while the Knowledge Panel is like a single book or page extracted from that library to answer a specific query.
How the Knowledge Graph Impacts SEO
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) has always been about understanding and adapting to the algorithms and features of search engines to ensure visibility and relevance. With the advent of Google’s Knowledge Graph, the landscape of SEO underwent a significant transformation. Here’s how the Knowledge Graph impacts SEO:
- Shift from Keywords to Entities: Traditional SEO heavily relied on keyword optimization. With the Knowledge Graph, the focus shifted towards understanding entities and their relationships. This means content creators need to ensure their content is contextually rich, covering topics comprehensively rather than just targeting specific keywords.
- Enhanced Search Results: Knowledge Graph results, often displayed as Knowledge Panels, provide users with quick answers. While this improves user experience, it might reduce the click-through rate to websites since users can get the information they need directly from the search results page.
- Importance of Structured Data: The use of structured data markup (like Schema.org) has become more crucial. By marking up content, webmasters can provide explicit clues to Google about the meaning of a page, helping it to better understand and represent content in the Knowledge Graph.
- Authoritativeness and Credibility: The Knowledge Graph prioritizes information from reputable sources. Ensuring that content is accurate, well-researched, and comes from authoritative sources can increase the chances of it being recognized and utilized by the Knowledge Graph.
- Local SEO Implications: For local businesses, the Knowledge Graph can display essential details like business hours, location, reviews, and more. Keeping this information updated on platforms like Google My Business becomes paramount.
- Brand Visibility: Brands with a well-defined presence and information can benefit from the Knowledge Graph as it can showcase brand-related details, products, services, and more, enhancing brand visibility in search results.
- Voice Search and Virtual Assistants: As voice searches become more prevalent with devices like Google Home and smartphones, the Knowledge Graph plays a pivotal role. It provides concise answers that these devices read out to users, emphasizing the need for content to be optimized for voice search.
- User Engagement Metrics: Since the Knowledge Graph aims to provide the best answers, metrics like user engagement, dwell time, and bounce rate become even more critical. High-quality, engaging content is more likely to be favored.
In conclusion, the introduction of the Knowledge Graph has reshaped the SEO landscape, emphasizing context, relevance, and the interconnectedness of information. SEO professionals and content creators need to adapt their strategies, focusing on providing comprehensive, authoritative, and structured content to align with the Knowledge Graph’s objectives and ensure continued visibility and relevance in search results.
Some Benefits of the Knowledge Graph (for Google)
The Knowledge Graph, since its inception, has been a game-changer for Google, revolutionizing its search capabilities and user experience. But what are the direct benefits for Google itself? Let’s explore the advantages that the Knowledge Graph brings to the tech giant.
Scaling Benefit
- Massive Data Handling: As the internet continues to grow exponentially, the amount of information available is vast. The Knowledge Graph allows Google to handle this immense data efficiently, categorizing and structuring it in a way that makes it accessible and useful.
- Adaptable to New Information: With new entities, facts, and relationships emerging daily, the Knowledge Graph’s architecture is designed to scale and incorporate this fresh data seamlessly.
- Reduced Redundancy: By understanding entities and their interrelations, the Knowledge Graph can minimize data redundancy, ensuring that the same piece of information isn’t stored multiple times in different contexts.
Diversity of Data Sources Benefit
- Richer Information Pool: Google’s Knowledge Graph aggregates data from a multitude of sources, ensuring a comprehensive and diverse information repository. This diversity ensures a holistic view of entities and topics.
- Credibility and Accuracy: By pulling from various reputable sources, the Knowledge Graph ensures the information’s credibility and accuracy, reinforcing Google’s position as a reliable search engine.
- Dynamic Updates: The diverse range of data sources ensures that the Knowledge Graph remains updated with the latest information, be it news events, scientific discoveries, or cultural shifts.
Information Integrity Benefit
- Consistency in Data: The Knowledge Graph ensures that the information presented is consistent across various queries. For instance, details about a historical event will remain consistent, whether the search is about the event itself or a related figure.
- Error Corrections: With its vast interconnected database, inconsistencies or errors in data can be identified and rectified more efficiently, ensuring information integrity.
- User Feedback Integration: Google allows users to provide feedback on Knowledge Panels. This direct user input helps in further refining the data, ensuring its accuracy and relevance.
Information Retrieval (Speed) Benefits
- Instant Answers: One of the Knowledge Graph’s most noticeable benefits is the speed at which it provides answers. Users often get direct answers to their queries right on the search results page, enhancing the search experience.
- Efficient Algorithms: The structured nature of the Knowledge Graph enables Google’s algorithms to quickly identify and retrieve relevant information, reducing the time taken to generate search results.
- Optimized Performance: The Knowledge Graph’s design ensures that, despite its vast size, data retrieval remains optimized, ensuring that Google’s performance remains swift and efficient.
In essence, the Knowledge Graph offers Google numerous advantages, from handling vast amounts of data efficiently to ensuring information integrity and speedy retrievals. It reinforces Google’s commitment to providing users with accurate, relevant, and quick answers, further cementing its position as the leading search engine.
How to Optimize for the Knowledge Graph
With the increasing prominence of the Knowledge Graph in Google’s search results, it’s crucial for businesses, brands, and individuals to optimize their online presence to be favorably represented. Here’s a guide on how to optimize for the Knowledge Graph:
Claim and Edit Your Knowledge Panel (if Applicable)
– Verification Process: If you’re a notable person, organization, or brand, you might already have a Knowledge Panel generated by Google. Start by claiming it. Google provides a verification process to authenticate your identity and grant you editing access.
– Update Information: Once verified, ensure that all details in the Knowledge Panel are accurate. This includes basic information, images, associated links, and more.
– Regularly Monitor: Trends, news, or significant events can influence your Knowledge Panel. Regularly check and request updates if necessary to ensure it remains relevant and accurate.
Get Links from Reputable Sites
– Boost Credibility: One of the ways the Knowledge Graph determines the reliability and authority of information is by evaluating the quality of sites linked to it. Being referenced or linked from reputable websites can boost your entity’s credibility in the eyes of the Knowledge Graph.
– Engage in Ethical SEO: Focus on generating genuine, high-quality backlinks. Avoid black-hat SEO techniques, as these can harm your reputation and visibility.
– Guest Blogging and Partnerships: Collaborate with authoritative sites in your industry for guest blogging opportunities or partnerships, which can result in valuable backlinks.
Use Structured Data for Organization
– Implement Schema Markup: Schema.org provides a collection of shared vocabularies webmasters can use to structure metadata on their webpages. Implementing this markup helps Google better understand the content, making it more likely to be incorporated into the Knowledge Graph.
– Highlight Key Information: Use structured data to emphasize essential details about your entity, such as official names, addresses, founding dates, or other pertinent facts.
– Test and Validate: Google provides tools like the Structured Data Testing Tool to validate your markup, ensuring it’s correctly implemented.
Set Up a Google Business Profile (if Applicable)
– Local SEO: For local businesses, a Google Business Profile (formerly Google My Business) is crucial. It ensures your business details like location, hours of operation, and customer reviews are accurately represented in the Knowledge Graph.
– Engage with Reviews: Regularly monitor and respond to reviews on your Google Business Profile. Positive engagement can influence your online reputation and visibility.
– Update Regularly: Ensure that all information on your profile, including photos, services, and promotions, is regularly updated and accurate.
In conclusion, optimizing for the Knowledge Graph requires a combination of ensuring accurate representation, building authority through quality backlinks, using structured data for better content understanding, and leveraging tools provided by Google. By following these steps, entities can enhance their visibility and representation in Google’s search results.
How it Works: Where You See Google’s Knowledge Graph Used
Google’s Knowledge Graph is not just a behind-the-scenes feature; its influence is evident in various components of the Google ecosystem. Here’s a breakdown of where you can typically see the Knowledge Graph in action and how it enhances the user experience:
1. Search Results Page (SERP):
- Knowledge Panels: These are the most visible representation of the Knowledge Graph. When you search for a notable person, place, organization, or thing, a box might appear (usually on the right side of the search results on desktop) providing a concise overview of the entity.
- Instant Answers: For specific queries, Google provides a direct answer at the top of the SERP, sourced from the Knowledge Graph. For instance, “What’s the capital of France?” will yield “Paris” as a direct answer.
2. Google Images:
- When you search for an entity, the images displayed are often sourced based on the Knowledge Graph’s understanding of that entity, ensuring relevancy.
3. Google Maps:
- Information about places, landmarks, businesses, and more on Google Maps is enhanced by the Knowledge Graph. It provides context, related places, historical data, and other relevant information about a location.
4. Google Assistant and Voice Search:
- When you ask Google Assistant a question, the concise and accurate answers it provides often come from the Knowledge Graph. It’s especially evident in responses to factual questions or queries about notable entities.
5. Google Discover:
- This feature, available on mobile devices, curates content based on user interests. The Knowledge Graph plays a role in understanding topics and entities of interest, ensuring the content displayed is relevant to the user.
6. YouTube:
- Google’s Knowledge Graph assists in understanding video content, context, and topics. It can influence video recommendations and search results on YouTube, ensuring users find content that aligns with their interests and queries.
7. Google News:
- The Knowledge Graph aids in categorizing news articles based on entities and topics, ensuring users receive news relevant to their interests or global events.
8. Google Ads:
- Advertisers can benefit from the Knowledge Graph’s understanding of user intent and context, allowing for more targeted and relevant ad placements.
In essence, the Knowledge Graph is deeply woven into the fabric of various Google services. It acts as the backbone that ensures users receive accurate, relevant, and contextually appropriate information, whether they’re searching for a historical fact, looking for a local restaurant, or watching a video on YouTube. Its integration across the Google ecosystem underscores its importance in providing a seamless and enriched user experience.
Google SERP Checker to Monitor Your Website’s Ranking on Google SERP
The Google SERP Checker is crucial for SEO professionals and website owners to assess their website’s visibility in Google search results. It instantly shows where a webpage ranks for specific keywords, helping users understand their website’s real-time performance. This information is vital for refining SEO strategies and pinpointing areas needing improvement to enhance search rankings.
The tool goes beyond basic rank tracking, offering features like historical rankings, competitor analysis, and keyword trends. Users can observe ranking fluctuations, benchmark against competitors, and grasp keyword trends for informed decision-making. This comprehensive analysis enables proactive SEO strategies, boosting traffic and online visibility.
Track Your Google Position!
Maximize your SEO results with our comprehensive Google SERP Checker.
Conclusion
The Google Knowledge Graph represents a monumental leap in the realm of search technology, reshaping how users receive and interact with information online. By understanding and mapping the intricate relationships between vast amounts of data, it offers a more contextually rich and nuanced search experience. Its influence permeates various Google services, ensuring that whether you’re seeking a quick answer, exploring a new topic, or diving deep into research, the Knowledge Graph is there to guide and inform. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the Knowledge Graph stands as a testament to Google’s commitment to making the world’s information universally accessible and useful.