What Is Cookie Lookup?
Let’s start with an explanation of what cookies are and how they work. It is most often an HTTP cookie, also known as a web cookie or a browser cookie, that is referred to when the term “cookie” is used in connection with website maintenance (Chrome, Firefox, etc.) of it is also called text files with small pieces of data. In actuality, it is a one-of-a-kind tag that websites place on the computer of the user to get insights on their behavior patterns. In the event that a user returns to a specific URL, text files with small pieces of data allow the website to “remember” that user and provide them with information that was previously found valuable (login, password, etc.). When users return to a website, cookies are used to identify them (authenticate them) and display “personalized” pages that are tailored to their specific requirements and interests.
For more info about “How To Delete Cookies On Google Chrome”, watch the video by Tech Insider.
Cookies are classed according to the following criteria:
- Session Cookies: These cookies remain active, as long as the console that triggered it is open. This session these text files with small pieces of data are removed when the user quits the browser.
- Persistent Cookies: These text files with small pieces of data are stored on the user’s computer indefinitely and can last for months or years.
Cookies are required by law for a website to function correctly — for example, the ones that check to see if you have already logged in. Non-essential cookies are not required for a website to function. They are frequently introduced by the website to provide new features — for example, the text files with small pieces of data that enable the pop-up adverts that testers see on some websites.
The website that the user or finder is now browsing sets first-party cookies. They provide services such as monitoring login status and storing shopping cart contents. Third-party cookies are those that are placed by other websites or third-party tools in order to track user behavior on the present site. For example, Google Analytics cookies test and audit users in order to measure conversions.
When the browser is closed and the session ends, the session cookies expire. Session cookies, for example, could be on a shopping website and keep the products in the cart even if the user navigates to a different page. Persistent cookies, on the other hand, remain on the user’s browser for a longer amount of time and only expire when the expiration date specified to them is reached. Unlike session text files with small pieces of data, persistent cookies keep the products and shopping statistics in the online shopping cart when the user closes the browser, allowing them to be accessed on the next visit.
What Is a Cookie Checker?
A cookie checker is a tool that gives detailed information about all text files with small pieces of data that have been saved by a specific website during your session. The tool is an identifier that displays text files with small pieces of data on the screen and checks if the website is safe.
Using a Cookie Checker Tool (How To Use)
Step 1: Insert your URL
When an address is added to the cookie checker, you will receive a result similar to the one shown below.
Step 2: Interpreting the cookie checker tool results
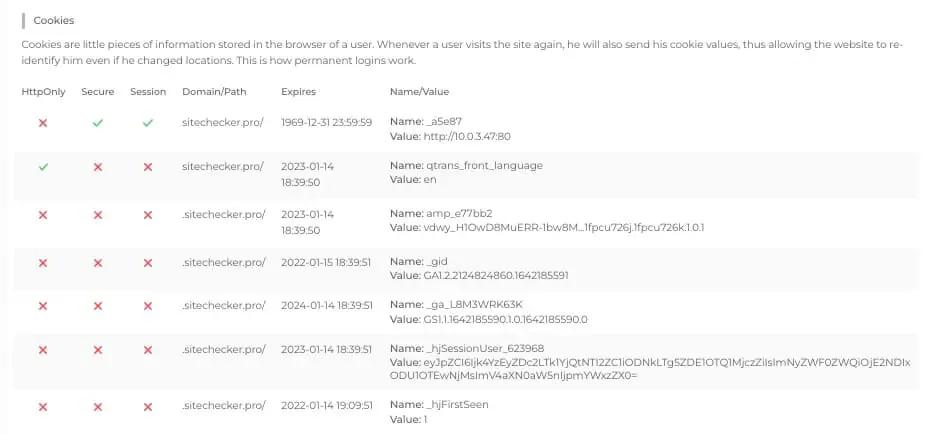
Cases When a Cookie Check Is Needed
Is it possible to remove text files with small pieces of data from a computer? Most modern browsers let you select whether to accept or reject cookies, and you can delete it from your browser’s “history” menu after each online session.
In the end, which regulations you follow determines a great deal. In some circumstances, detecting and deleting cookies can make using a website’s functionality, such as a shopping cart, more difficult. Accepting logger text files with small pieces of data in some situations allows advertisers to follow their behavior for their gain rather than the users’.
Cookies are designed to be useful, and they are utilized more often than you might think. Here are some examples of when the files have been saved on your system and need to be removed.
Shopping. Cookies assist you in placing things in your “virtual shopping basket” on retail sites. With the help of text files with small pieces of data, you can browse a website that displays items and add or remove them from your shopping basket at any time.
Sign-ups.Text files with small pieces of data make logging into websites a breeze. When you log in to a website with your username and password, they help by alerting the website that you are already authorized, allowing you to perform things that only registered customers (who are signed in) may do.
Personalization. Websites also use text files with small pieces of data to customize content based on user choices. Google, for example, allows you to select the number of entries per page that you want to see.
Research and relevance. Marketers and advertisers use cookies to regulate your online behavior and transmit that information to the advertiser. Based on that information, an advertiser may be able to select what type of ads to run on a web page while you are online. It’s no coincidence that an ad for a particular brand of shoes or computer displays on a webpage’s sidebar after you look it up.
Different Types of Cookies
Text files with small pieces of data are used for a number of reasons, but they all work in the same way:
- Data packets that are sent and received unmodified were referred to as “magic cookies” in the early days of computing. This was a sign and a frequent method of gaining access to computer database systems, such as those on a company’s internal network. This concept predates the modern conception of a “cookie.”
- HTTP cookies are a repurposed version of the “magic cookie” designed specifically for online use. In 1994, web browser programmer Lou Montulli was inspired by the “magic cookie.” When he was assisting an online buying site with their overloaded servers, he recreated this concept for browsers.
HTTP cookies are currently used to administer online experiences. Some malicious parties can use it to analyze internet activities and steal personal information.
The Other Ways to Check Cookies
Google Chrome:
Open a new Private window and explore your website’s URL. Launch the Developer Tools app. This depends on your browser. Chrome: View > Developer > Developer Tools, or CMD + ALT + I on Mac, or F12 on Windows.
Firefox:
With Mozilla Firefox, you can examine the text files with small pieces of data and the domains they are sending data to. Open a new Private window and explore your website’s URL. Launch the Developer Tools app. Press CMD + ALT + I or F12 on a Mac or PC to open the Storage Inspector in Firefox.
Safari:
In Safari, follow these steps to examine the cookies and the domains they are sending data to:
Open a new Private window and explore your website’s URL. Launch the Developer Tools app. Press CMD + ALT + I on a Mac or F12 on a PC to open the Web Inspector in Safari.
Correctly cookies settings it is an important, but it is not a main in your SEO!
Make that full site audit to check out other technical parts of your SEO and fix them.