What is a Large Sitemap Size?
Google used to allow sitemaps to reach a maximum of 10MB per map. Later, Google changed the limit, and it went up to 50MB. It means that today, the max URL number goes up to only 50,000 URLs.
On the rare occasion that it becomes too big, you’ll receive an error saying your XML files are too large.
What Triggers it?
When you create a website with a sitemap, it has only one by default. It grows when you add many posts, image files, videos, and other entries to your site. When you enable website structure indexes, you automatically allow the all-in-one SEO composer to split it into smaller parts. Splitting it is the best and safest way to deal with a size that goes beyond the limit. However, you still need to manage your navigation map file size, as large files slow down web crawlers.
How to Check the Issue
In reality, it’s not often that people receive an error about a site index that has grown large enough to surpass its typical limits. But in case the event occurs, you know what you should do to deal with it effectively. The limits mentioned above are important, as they keep your web servers from running slowly. If you notice your website taking forever to load, it can be an indication of a large sitemap.
In the Sitechecker SEO tool, under the “XML sitemaps” section, you can see a focused approach to identifying and addressing specific sitemap issues on your website. This section of the tool specializes in spotting and listing problems that might hinder the effective indexing of your pages by search engines. For instance, it flags issues like the absence of a link to the XML sitemap in the robots.txt file, which is crucial for search engine crawlers to locate and scan your sitemap efficiently. Additionally, it identifies redirects within XML sitemaps, which can mislead or confuse crawlers, potentially leading to poor indexing.
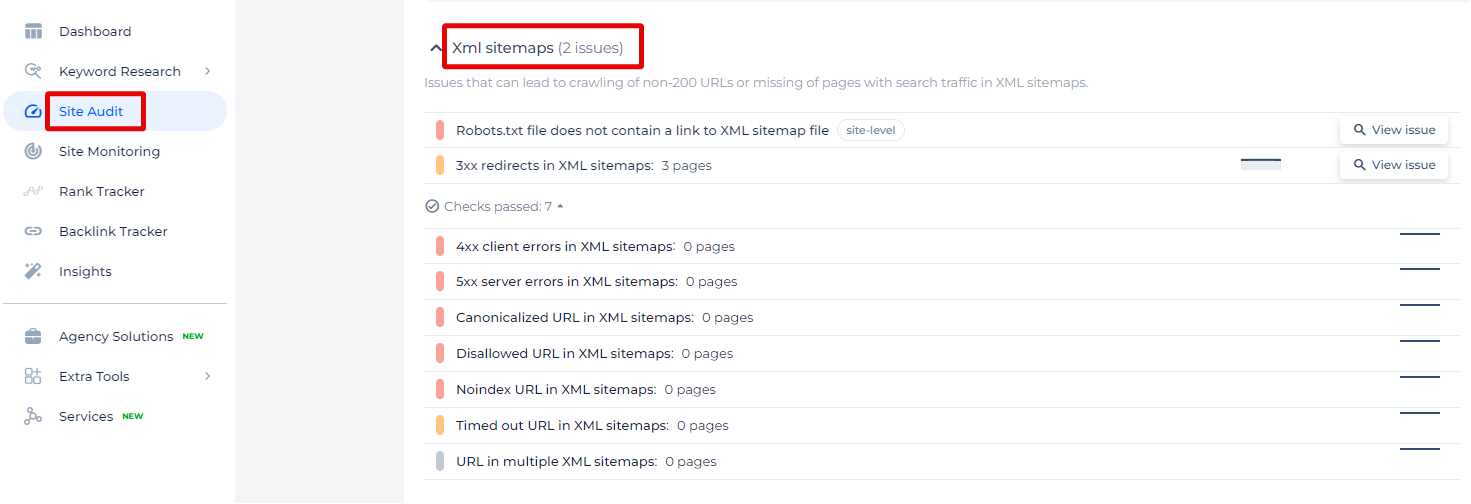
By clicking on the “View issue” link next to each problem, you’re directed to a detailed page where you can see a comprehensive list of affected pages and receive specific guidance on how to rectify these issues.
Enhance Your SEO with Effective Sitemap Audits!
Our Site Audit Tool offers detailed diagnostics and solutions for sitemap issues.
How to Fix and Simplify Sitemap Size
To fix and simplify the size of your website structure, follow these steps:
1. Remove Unnecessary URLs
Audit Your navigation map, and remove outdated or irrelevant URLs.
Focus on Key Pages: ensure only the most important pages are included.
2. Break Down Large Sitemaps
If your navigation map file exceeds the 50,000 URL or 50MB limit, break it into smaller files and use it to reference them.
<sitemapindex xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<sitemap>
<loc>http://example.com/sitemap1.xml</loc>
</sitemap>
<sitemap>
<loc>http://example.com/sitemap2.xml</loc>
</sitemap>
</sitemapindex>
3. Optimize URL Entries
- Remove Query Parameters: If possible, avoid URLs with unnecessary query parameters.
- Canonical URLs: Ensure each URL is canonical and unique.
4. Prioritize Key Content
Include High-Priority Pages: Ensure high-value content, such as new articles or top-performing pages, is prioritized.
5. Use Automated Tools
Sitemap Generators: Use automated tools or plugins (like Yoast SEO for WordPress) to generate and manage site guides efficiently.
6. Compress Sitemap Files
GZIP Compression: Compress your files using GZIP to reduce file size and speed up download times.
gzip on;
gzip_types application/xml;
7. Regular Updates and Maintenance
- Schedule Regular Audits: Regularly review and update your web map to ensure it reflects the current state of your website.
- Automate Updates: Use tools or scripts to automatically update your navigation map file when content changes.
8. Validate Your Sitemap
Use XML Sitemap Checker to validate and test for errors.
By following these steps, you can effectively fix and simplify your navigation map file, ensuring it remains manageable, efficient, and beneficial for your website’s SEO.
Final Idea
To manage and optimize large sitemaps for better SEO and website performance, split files exceeding 50,000 URLs or 50MB into smaller files. Regularly audit and remove unnecessary URLs, prioritize key content, and use automated tools like web map generators. Compress files with GZIP and schedule regular updates to maintain efficiency. Use tools like Sitechecker SEO to identify and fix issues, ensuring proper indexing by search engines. Validate navigation maps with XML Sitemap Checker to maintain accuracy and functionality.