You want elements of your website pages to display correctly on different devices. So, it would help if you used the initial scale in the viewport meta tag.
What Does “The Initial Scale in the Viewport Meta Tag is not Working” Mean?
This means that the URL in question does not contain the initial scale in the HTML document. Or, this element is on the page, but you set it to a value other than 1.0. Besides, the initial scale is an optional attribute for the viewport meta tag that helps control the zoom level when the page is first loaded.
You can discover more details about using the initial scale here.
Also, you can watch a video tutorial by Matt Cutts from Google to discover how much time you should spend on meta tags.
What Triggers This Issue?
You want your web and mobile pages to display at the same standard size on the first load. But for some reason, they don’t act as you want. The following are possible reasons:
- Multiple viewport meta tags were found in the <head> of a HTML document
- No initial scale is recognized
- The initial scale is found with a value other than 1.0
How to Check the Issue?
You can go to your website page from your computer, press Ctrl+U, press Ctrl+F, and enter “initial scale” in the field. Then you will see one of the possible reasons for incorrect scaling, which we described in the previous block. In addition, you need to check with the rest of the pages of your site so that the initial scale is not ignored there.
Or you can use Sitechecker to track various viewport-related problems.
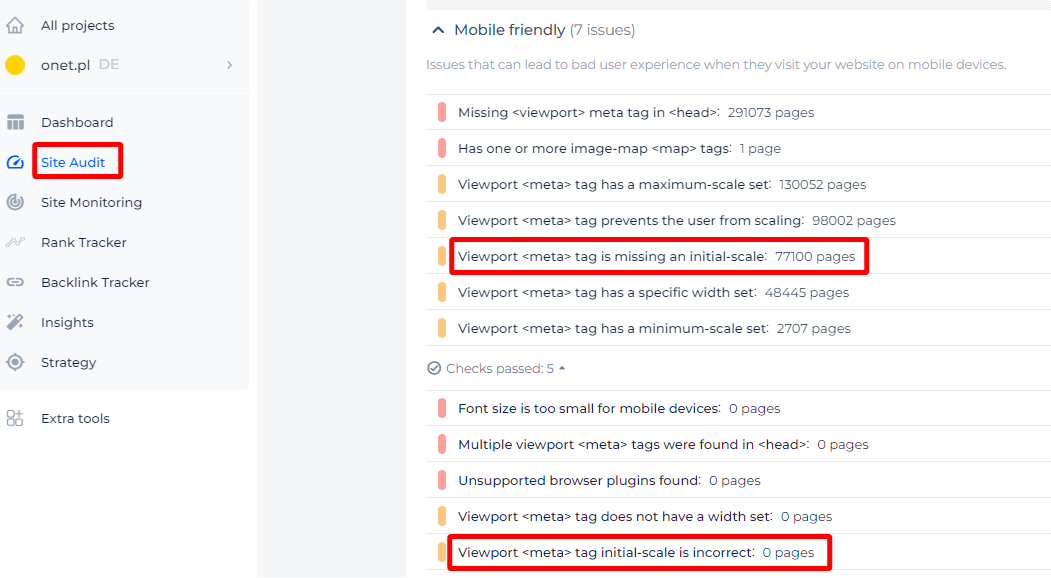
If you delve deeper into a problem, you will find a list of impacted pages along with the option to see their source code.
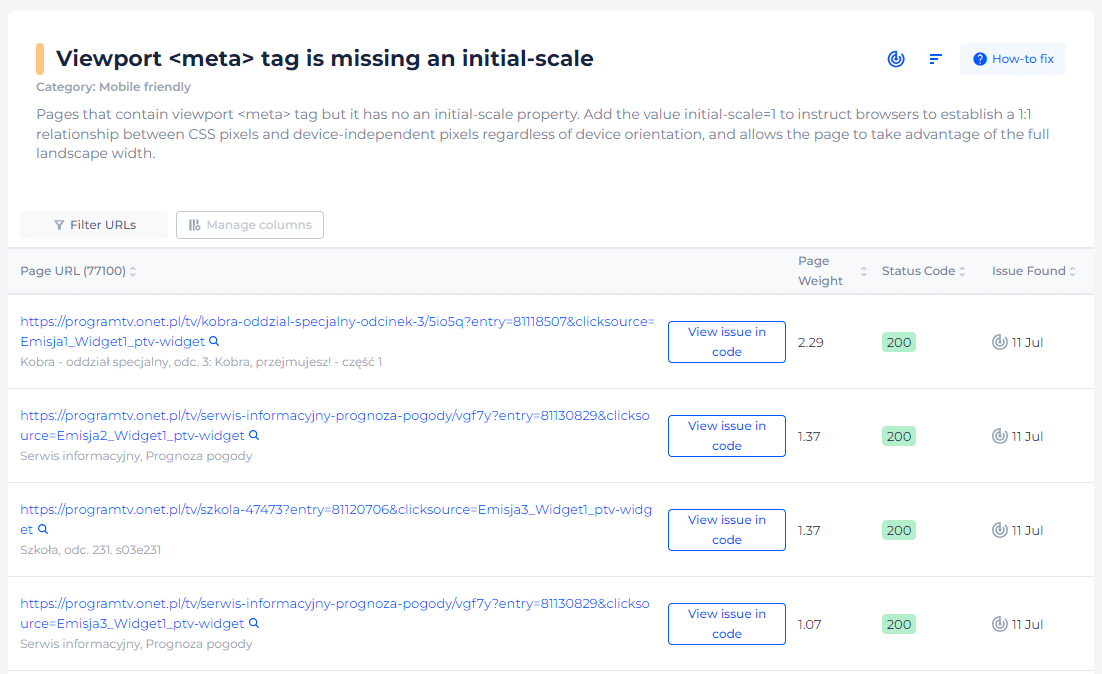
Ensure your site starts off on the right scale!
Is your viewport's initial scale set correctly? Don't guess, check it with Sitechecker!
Why is This Important?
The initial scale allows all elements on your page to display correctly when users visit your site. from different devices. In this case, text, buttons, icons, and images do not overlap. Moreover, the maximum scale can also fit your site if you want to add the scaling of your pages for users. You may need to set here such a value at which the content on the site will also be displayed right.
How to Fix the Issue?
To fix the issue “Viewport Meta Tag is Not Working,” you need to ensure that the viewport meta tag is properly implemented and correctly configured in your HTML. Here are some common troubleshooting steps and tips to resolve this issue:
1. Correct Placement in HTML
Ensure that the viewport meta tag is placed inside the <head> section of your HTML document. It should look like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Your Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Your content goes here -->
</body>
</html>
2. Correct Syntax
Ensure the syntax of the viewport meta tag is correct. A common and widely used configuration is:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
3. No Conflicting Tags
Ensure there are no conflicting meta tags or settings. Having multiple viewport meta tags or other tags that might override the viewport settings can cause issues. Only include one viewport meta tag:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
4. Clear Browser Cache
Sometimes, browser cache can cause issues with rendering the updated meta tag. Clear your browser cache or try accessing your site in an incognito/private browsing window.
5. Ensure No CSS or JavaScript is Overriding
Make sure no CSS or JavaScript is overriding the viewport settings. For instance, check for any CSS rules that might affect the layout:
html, body {
width: 100%;
max-width: 100%;
}
Also, ensure no JavaScript is modifying the meta tag dynamically in a way that breaks the intended functionality.
6. Check for Issues on Mobile Devices
Test your website on multiple mobile devices and simulators to ensure the viewport meta tag works correctly across different screen sizes. Tools like Chrome DevTools Device Mode can help simulate various devices.
7. Use the Correct Values
Ensure you are using appropriate values for your use case. Some common configurations are:
For responsive design:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
For non-responsive design (fixed width):
<meta name="viewport" content="width=1024">
For disabling zoom:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no">
8. Validate HTML
Use an HTML validator to check your HTML for any syntax errors that might be causing issues. You can use the W3C Markup Validation Service.
9. Check for Compatibility Issues
Ensure that the meta tag is compatible with the browsers you are targeting. While modern browsers widely support the viewport meta tag, some older browsers might have issues.
By following these steps, you should be able to identify and fix the issue with the viewport meta tag not working as expected. If the problem persists, you might want to look into any specific quirks or bugs related to the browsers or devices you are testing on.