What is the URLs with Redirect Chains issue?
A URL with a redirect chain issue is a situation where a URL does not point directly to the intended final destination. Instead, it goes through one or more intermediate URLs before reaching the end destination. This can cause several problems for both users and search engines.
This issue occurs when a URL forwards to another URL, which then redirects again. Common causes include website redesigns, rebranding, content restructuring, platform migration, and mismanagement of redirects. Stacking redirect rules and changing temporary redirects to permanent ones without updates also contribute. Content updates, expired pages, and marketing campaigns can introduce additional redirects.
How to Check the Issue
To check and fix the issue, follow these steps:
Checking for Redirect Chains
1. Use Sitechecker to crawl your website and identify redirect chains.
Chains could be created accidentally and unknowingly, especially when dealing with big sites. Having forwardings between the following links isn’t an issue: A–>B and B–>C or X–>Y and Y–>Z. But as soon as you try to redirect URL C to URL X, you suddenly create a chain with 4 redirects and indexing on URL X might fail or this link could be even removed from the index altogether.
Therefore, one should examine the redirects for potential long chains and consider better forwarding strategies with fewer intermediary steps. Ideally, the redirect target of the first URL should be the final destination URL.
Take care to not just remove redirects of intermediary pages since there could be other places linking to this URL. If redirects are removed without substituting with alternate strategies, expect broken links and 404 errors.
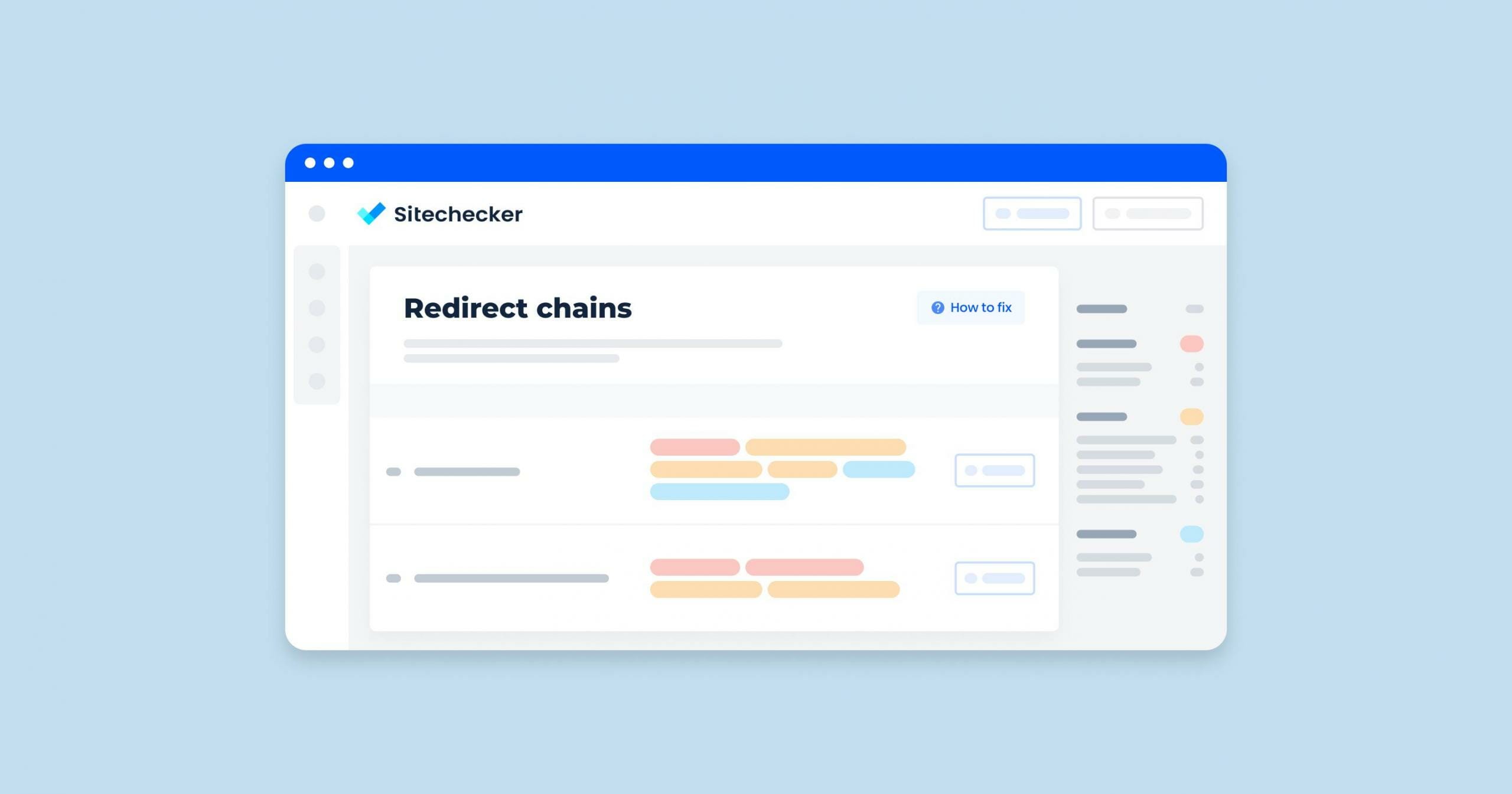
In the Site Audit section of our SEO tool, we have identified an issue categorized under “Redirects” which is crucial for maintaining an efficient and user-friendly website. This specific issue, labeled as “Redirect chains,” indicates that there are multiple consecutive forwardings from one URL to another.
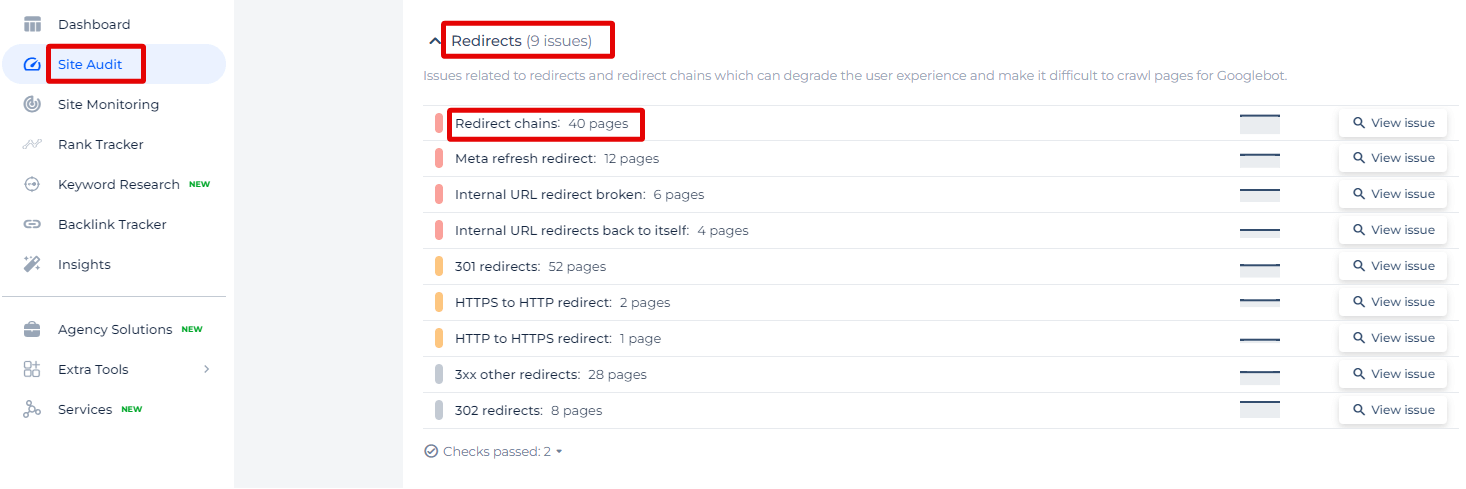
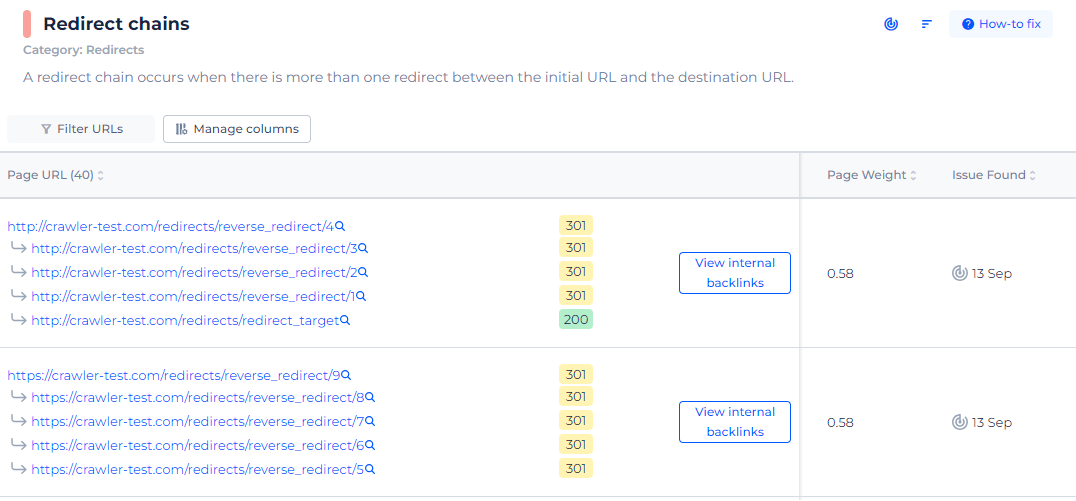
By selecting “View issue,” you can access a detailed list of all pages affected by redirect chains. This list is not just a count; it presents each URL that is part of a redirect chain and allows you to investigate the sequence of redirects to understand the path a user or search engine would take through your site. This information is vital for diagnosing and resolving the identified SEO issues, making your website more accessible and easier to index.
Unravel Redirect Mysteries!
Uncover the secrets behind your website's redirect paths. Simplify complex URLs with our Redirect Checker today!
2. Analyze Redirect Paths
Map out the sequence of redirects for identified chains. Identify the start and final destination points of each chain.
1. Map the Sequence
- Start with the initial URL: http://example.com/old-page
- Note the first redirect: http://example.com/old-page → http://example.com/new-page
- Identify the second redirect: http://example.com/new-page → https://example.com/new-page
- Identify the third redirect: https://example.com/new-page → https://example.com/final-page
2. Identify Start and Final Points
- Start Point: http://example.com/old-page
- Final Destination: https://example.com/final-page
Fixing Redirect Chains
1. Update Redirect Rules
Replace intermediate redirects with direct ones from the original URL to the final destination. Ensure that each URL points directly to the final URL without intermediate steps.
2. Implement 301 Redirects
Use 301 (permanent) redirects to ensure search engines pass link equity to the final URL. Edit your server configuration files (.htaccess for Apache, nginx.conf for Nginx) or use server-side scripting.
Apache (.htaccess):
Redirect 301 /old-page http://example.com/final-page
Nginx (nginx.conf):
rewrite ^/old-page$ http://example.com/final-page permanent;
3. Update Internal Links
Change internal links to point directly to the final URLs, reducing the need for redirects.
4. Re-crawl and Test
After updating redirects, re-crawl the website to ensure issues are resolved. Verify there are no broken links or additional redirect chains.
5. Monitor Regularly
Continuously monitor your site for new redirect chains and address them promptly to maintain optimal performance.