You’ve probably noticed that some websites do or do not contain the WWW. Is there a difference between websites that do or do not use this URL type? Every SEO and marketing expert has wondered how this element can be used to their advantage for search engine promotion.
At this point, we can’t say with certainty which type of URL — WWW or non-WWW — should be used for your website. They both have advantages and disadvantages. Some site owners add this part to their address for the convenience of their users or brand consonance. If you’re just planning to start working on your website, you’ll want to research information about WWW. So that you can make a choice about whether to use this fragment in your website address or not. In terms of search engine optimization, WWW domains generally have advantages even capable of improving the performance of your website.
At the same time, URLs, both with and without the WWW, have their pros and cons. We advise you not to change the URL when making a website migration by adding or removing WWW from it. Search engines such as Google or Bing will consider the presence of this fragment as two different sites. It can lead to problems with the occurrence of duplicate content. There are also methods to work with either option for your website. Using the All-in-One SEO plugin for the WordPress console will automatically set the canonical URL in the site header and tell the search engine the correct version.
We’ve created a unique free WWW Redirect Checker tool that will allow you to get information about the canonical version of your website. In this article, we will explain how to use the tool. In addition, we will compare URLs with and without WWW and list the advantages of both in terms of search engine optimization.
WWW Redirect Checker Tool: A Step-by-Step Guide
Well, if you are interested in the influence of the WWW fragment in your website’s domain, then our new WWW Redirect Checker tool will help you. Uses testing in this tool to check the canonical version of your domain. Simply check your website for possible URL canonicalization problems.
Canonicalization shows how a web site can use slightly different URLs for the same page (for example, http://www.example.com and http://example.com mean the same page). If this happens, search engines may not recognize which URL is correct for indexing.
To avoid this issue, we created our WWW Redirect Checker. Below, using our sitechecker.pro as an example, we will tell you how to use the tool for your daily SEO tasks.
Step 1: Insert your URL
Open the tool page. Here you will see an empty line to enter the link you are interested in. Inserting the link will allow you to check for canonicalization problems. Click the blue arrow button to start scanning. To show you how the tool works, we decided to check our site, https://sitechecker.pro.
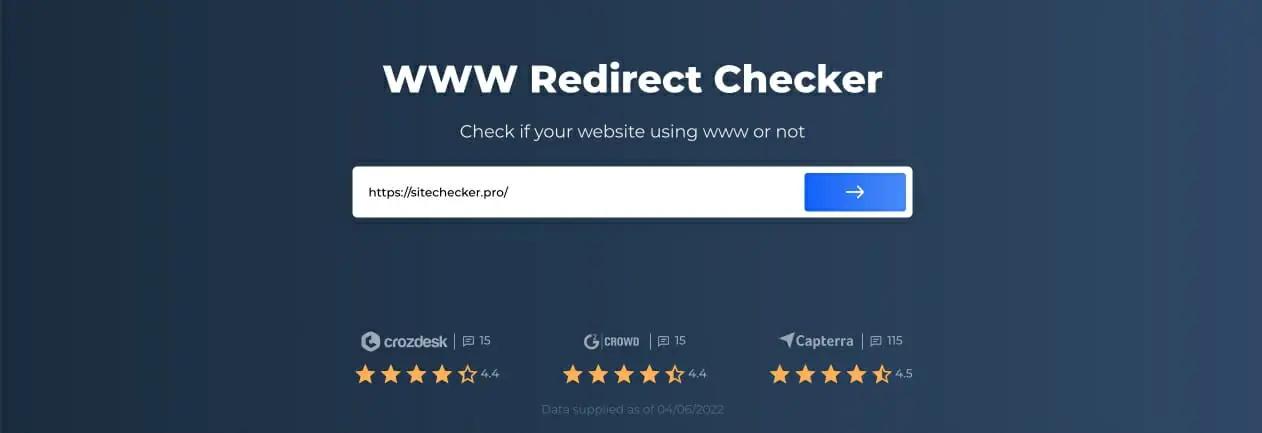
Step 2: Interpreting the WWW Redirect Checker Results
After the scan is complete, you can be reading if your page is canonical. The tool will also give you tips on using the WWW fragment in your site’s domain.
WWW vs. Non-WWW – Technical Differences
There is one technical difference between these two types of URLs, and as a rule, search engines are not definitive about their preference for one or the other. Before we get to the difference between http and https and the difference between WWW and non-WWW, here’s what the URL will look like to the user.
It is what URLs structure with WWW would look like:
- https://www.example.com
- http://www. example.com
URLs without a WWW :
- http ://example.com
- http://example.com
A domain without WWW is considered a “naked” domain. Adding the WWW prefix in front of the site name can help configure the domain name system (DNS) and limit cookies with more than one subdomain. Normally, small websites will not be affected no matter what format or IP you choose. Nevertheless, the WWW fragment in the URL will give more technical benefits when used on larger sites.
When you add this fragment in front of your site name, it takes on the role of the hostname. It can help you with DNS flexibility and restrict cookies when using multiple subdomains. Non-WWW domains have some technical limitations. For example, a CDN provider cannot redirect traffic from a faulty server to a functional one.
Still, these technical differences are only visible if your website receives millions of hits every day. WWW domains can serve as a hostname and may have several subdomains attached to them. When the Internet first appeared, website URLs started with WWW by default. However, after a while, users entered website names without this prefix in the search bar. Website creators noticed this trend and decided to eliminate the unnecessary elements.
So, from a practical point of view, there is no difference between a URL with or without the WWW. But the difference does exist, and it lies in the advantages in DNS configuration and the limitations of cookies when using other domains.
Therefore, it is necessary to note that search engines will consider different sites with the WWW as two different sites. It is why you need to specify which URL you prefer to be indexed by Google.
Pros and Cons of WWW vs. Non-WWW URLs
Now that we have outlined some minor differences between the two URLs site versions let’s discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both formats.
WWW URL Pros
- Many website owners are simply comfortable specifying a domain with WWW because not so long ago, all website URLs started with WWW;
- The WWW URL allows cookies to be set for the WWW subdomain;
- WWW subdomains are more flexible for DNS. Consequently, the experience of working with content delivery networks becomes much easier.
WWW URL Cons
- The WWW prefix may soon become obsolete because users do not enter it in Internet searches;
- The WWW makes the URL longer, which contradicts the recommendations of search networks — the shorter the URL, the better.
Non-WWW URL Pros
- It is easier for users to type such a domain in a search because it makes the domain name four characters shorter;
- Non-WWW URLs may also have subdomains, which you can put in the sitemap.
Non-WWW URL Cons
- A domain without WWW does not have cookies, restricted to the root domain only.
- Non-WWW have no CNAME records, so you cannot redirect traffic from one server to another. It makes CDN operation for such domains difficult.
WWW vs. Non-WWW – Which is Better in Terms of SEO?
As you can see, each format has advantages and disadvantages. But there is another important point to consider. How do these formats affect search engine optimization?
The main thing is that your site cannot be accessed by two URLs (WWW vs. Non-WWW). When both formats are active, the search engine network sees them as two different websites. You may have more problems with duplicate content.
When both domains with WWW and non-WWW are active simultaneously, duplicate content is created on one page, but the entire site is considered a duplicate. Such a site may fall under search engine sanctions and disappear from search results.
And because search engines see the two URLs as separate websites, they divide the link weight by two / Because of this your website does not get all the weight and traffic. If you have tested your site through the WWW Redirect Checker and find that it has duplicate URLs with and without WWW, you need 301 redirects from one version to the other, which is the primary version. To make 301 redirects, you can ask your developer to make some changes to your .htaccess file.
As you can see, it is impossible to say with certainty which of the domain name formats will be more effective in optimizing your site for search engines. The only fact is that you can not have two versions of the site simultaneously. It can lead to unpleasant consequences, such as sanctions from search engine networks and exclusion from search engine results. You will lose link weight, user traffic, and ranking in the eyes of search engines. That’s why we recommend you to use our free tool WWW Redirect Checker to determine the canonical version of the domain address. This way, you can avoid unpleasant problems with search engines.
Checking WWW Redirect is important but not enough to rank good enough!
Make a full audit to find out and fix your technical SEO in order to improve your SERP results.