One of the best practices in web development is to keep your URLs short and concise. This makes it easier to remember where certain content lives on your site, and it makes your pages load faster because you’re sending less data over the internet. A URL length checking tool will measure the length of any given URL and determine if it meets the requirements of Google, Yahoo, Bing, and other search engines — as well as those of social media sites like Facebook and Twitter.
What is a URL Length Checker?
A URL length checker is a tool that allows you to view the number of characters in a URL. By doing this, you can see whether it meets the URL length limit of search engines and make necessary changes for better website optimization. Most search engines allow a max URL text length of 2,000-2,500 characters. However, long URLs also tend to be cluttered with hyphens and underscores, which can make them hard to read and less likely to show up on a search results page than shorter alternatives.
You may need to break long URLs into several parts (for example, turning /about-us/ into /about/, /history/, and /requests/), or you may find that using an anchor instead of a path (e.g., #top) works better for displaying long information on a single web page. So URL structure is important.
Be sure to test how your page address looks in different browsers across different operating systems and how it looks for mobile users. For example, Mozilla Firefox has a 65,583 URL character limit, far more than any search engine, which means that your URL may rank differently.
How to Use the Tool?
Sitechecker allows you to keep track of how long your URLs are so that you’re in good standing with Google. While there is no specific number after which you might incur a penalty from Google, it’s best to err on the side of caution. Here is how to check URL length via Sitechecker:
Step 1: Insert your URL
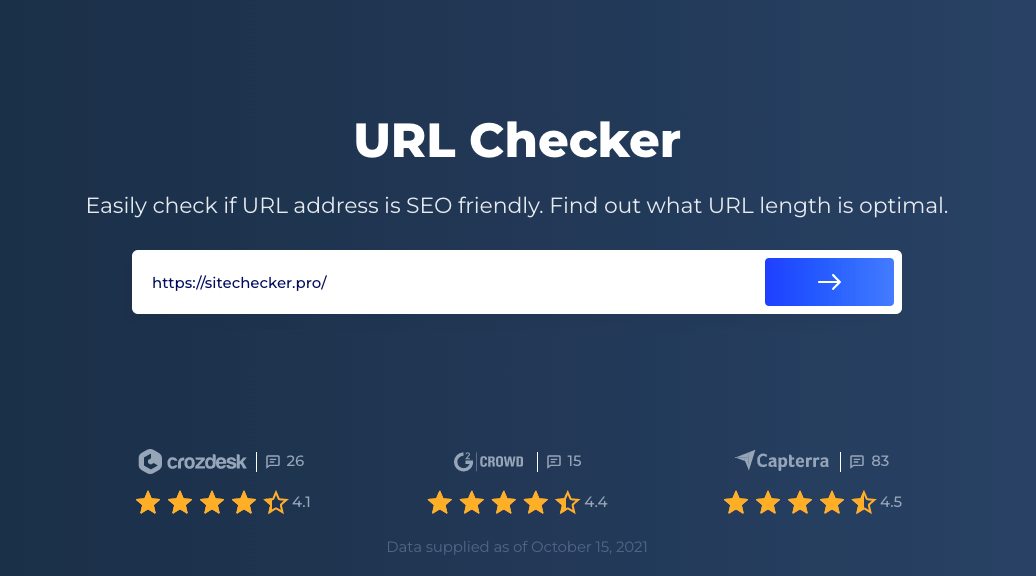
You can type any URL into this URL locator bar and click on the arrow to generate results.
Step 2: Get the result
URL Max Length Limits
Most search engines have a URL character limit of 2,000-2,500 characters. Long URL limits are pretty common for many web services (particularly social media sites), but they’re still a pain. The limit can be especially bad if you happen to be a photographer or you want to share links on places like Reddit and Imgur, where long page adress just don’t play well.
Does the URL Length Make it SEO Friendly?
What does Google say?
The direct answer is no. The URL length doesn’t matter. We use URLs as identifiers, it doesn’t matter how long they are. Personally, I try to keep them shorter than 1,000 characters, but that’s just to make monitoring easier. The number of slashes in there also doesn’t matter.
John Mueller, Google’s Search Advocate
Also, we have a detailed guide: “What is a URL: definition, structure, and examples & How to make it SEO friendly?” just check it out.
What does really important in URL for Google?
Google Chrome advises that all websites utilize https://. The hostname is the address of your website, which is usually the same as your email address. Google distinguishes between the www and non-www versions of a website (for example, www.example.com or just example.com). Experts recommend adding both the http:// and https:// versions of your website to Search Console, as well as the www and non-www variants.
The path, filename, and query string determine which material can be accessed from your web server. Because these three elements are case-sensitive, the URL for TITLE will be different than the URL for the title. The hostname and protocol are case-insensitive; therefore, capitalization doesn’t matter.
A fragment, for example, #info, indicates where the browser will scroll to on the page. Because the material is usually the same regardless of the fragment used, search engines normally ignore it. A trailing slash following the hostname is optional when linking to the homepage because it leads to the same content (https://example.com/ is the same as https://example.com). A trailing slash in the path and filename is interpreted as a distinct URL (indicating either a file or a directory); therefore, https://example.com/fish is not the same as https://example.com/fish/.
Detect not just URL length limit issue, but all types of URLs problems!
Crawl your site and find out all URLs with issues that can hart your users or your website SEO.
What do SEO experts say?
The length of a URL is an important factor in determining how user-friendly and readable it is, especially in social media. In the search engine optimization case, a lengthy URL might have some SEO advantages, such as keyword stuffing the URL, they will be highlighted and may provide additional relevance. Also, it can impact click rate. But overall, it is not the main factor and can harm your website’s usability, so you should keep the balance.
In this video, Darren Taylor, the owner of This Week In Digital, will explain in full detail the best practices.
Most experts are agreed that in URL length context you should keep the focus on:
Click rate
The click-through rate, or CTR, is extremely important in SEO. CTR refers to the percentage of people who clicked on your snippet in SERP. A low CTR can indicate the bad relevance of your snippet to the keywords and be the reason for the position’s downgrade.
CTR improvement is one of the foolproof techniques to improve your SEO ranking. Investing in it can result in a wide range of benefits, including higher SERP ranks, more traffic, and more conversions. Shorter URLs can lead to high click-through rates.
Social media displaying
Knowing social media character counts helps to gain more reach and engage visitors in posts. However, each social media platform has its own requirements. For example, Facebook allows a character limit of 63,206 in regular posts, whereas Instagram only allows 2,200 characters. Even so, shorter posts are always more engaging, and many experts agree that Facebook posts should be fewer than 50 characters.
But making the experiments is the only correct way to validate the information and get your own results.