What Does “4xx Page in the Sitemap” Mean?
A “4xx page in the sitemap” refers to a page listed in a website’s map that returns a 4xx HTTP status code when accessed. The 4xx status codes are part of the HTTP response codes indicating that there is a client-side error.
When a page that returns a 4xx status code is included in a sitemap, it can cause issues for search engines and affect the website’s SEO performance. Search engines like Google use website maps to discover and index the pages on a website. If they encounter a 4xx page, it can lead to wasted crawl budget and negatively impact the site’s indexing efficiency.
What Triggers This Issue?
Several factors can trigger the issue of having 4xx pages in a sitemap:
| Deleted Pages | If pages are deleted from the website but their URLs remain in the sitemap, accessing these URLs will result in a 404 Not Found error. |
| Moved or Renamed Pages | When pages are moved to a new location or their URLs are changed without updating the site index, the old URLs will return 404 errors. |
| Incorrect URL Entries | Typos or incorrect entries in the sitemap can lead to URLs that do not exist on the website, resulting in 4xx errors. |
| Access Restrictions | Pages that require authentication (401 Unauthorized) or are restricted (403 Forbidden) but are still included in the sitemap can trigger 4xx errors when crawled by search engines. |
| Expired Content | Content that is no longer available or has been deliberately removed can result in 410 Gone errors if the URLs are still listed in the site index. |
| Server Configuration Issues | Misconfigurations on the server can lead to certain pages returning 4xx errors even if the URLs are correctly listed in the sitemap. |
| Content Management System issues | Some CMS platforms might automatically generate sitemaps without removing old URLs, leading to 4xx errors when these URLs are accessed. |
| Manual Sitemap Updates | If the sitemap is updated manually, there is a higher chance of human error, leading to incorrect URLs that result in 4xx errors. |
How To Check the Issue
To get rid of any 4xx error codes, you need to find the source of the issue. One of the following actions will help you locate the problem:
If the sitemap cannot be accessed because of a 404 error, you can open it in an admin console. The status column will show you the issue. Open a list with URLs and find the one responding with an error.
Check your server logs. Open a log file and look for any 4xx errors.
Have a look at the configuration file: it’s either a .htaccess or nginx.conf file, depending on which server you’re using. The file may contain some unwanted redirects.
To find this issue on your website, use Sitechecker. The service allows you to scan the site and detect pages with 4xx client errors in XML sitemaps. You will find this issue in the section of sitemap-related problems.
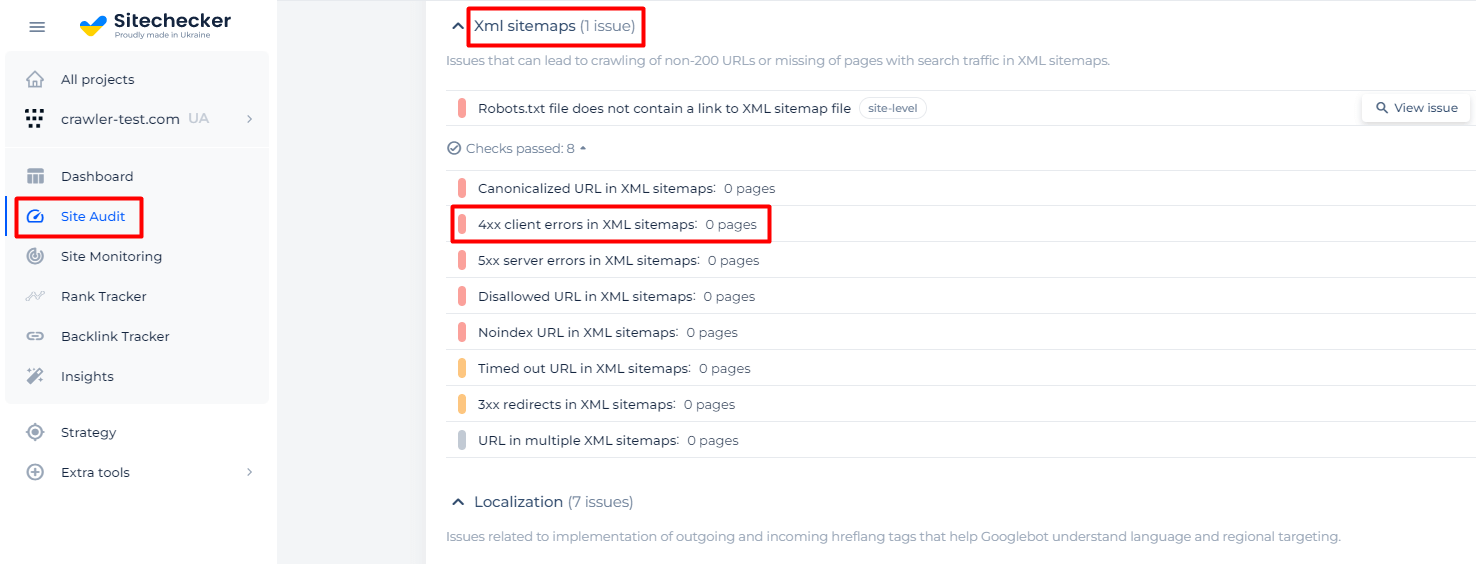
Detect 4xx errors being in sitemap as this is a serious technical issue on your site!
Crawl your site and find out all kind of issues that can affect your users or your website SEO.
How To Fix the Issue
To fix the issue of 4xx pages in the sitemap, follow these steps:
1. Identify 4xx Errors
Use tools like Sitechecker or Google Search Console to scan your site index and identify URLs returning 4xx errors.
2. Update or Remove Deleted Pages
If pages have been deleted, remove their URLs from the sitemap.
Implement 301 redirects for deleted pages to guide users and search engines to relevant content.
3. Fix Moved or Renamed Pages
Update the sitemap with the new URLs of moved or renamed pages.
Set up 301 redirects from old URLs to the new ones to ensure seamless navigation and preserve SEO value.
4. Correct URL Entries
Check the sitemap for any typographical errors or incorrect URLs and correct them. Ensure all URLs in the site index are valid and accessible.
5. Address Access Restrictions
If pages are restricted (401 or 403 errors), decide if they should be accessible to search engines. Adjust permissions or remove them from the sitemap accordingly.
For pages requiring authentication, ensure they are either accessible or excluded from the site index.
6. Handle Expired Content
Remove URLs of expired content that is no longer available from the sitemap.
If content is permanently removed, you can use a 410 Gone status and ensure it’s reflected in the sitemap update.
7. Server Configuration
Review server settings and configurations to prevent unintended 4xx errors. Address any server misconfigurations that might cause valid pages to return 4xx errors.
8. CMS and Plugin Management
Ensure your content management system (CMS) and any sitemap plugins are updated and configured correctly. Use automated sitemap generation tools that reflect real-time changes in the website structure.
9. Regular Audits
Regularly audit your sitemap to ensure all listed URLs are current and functional. Use Sitechecker to receive alerts on new 4xx errors and address them promptly.
10. Submit Updated Sitemap
After making updates, submit the revised sitemap in Google Search Console and other search engine webmaster tools to ensure they crawl the updated version.