What Does the “Oversized JavaScript Files” Issue Mean?
“Oversized JavaScript files” in a site audit refer to JavaScript files that are larger than optimal, potentially impacting the website’s performance. Here are some key points regarding oversized JavaScript files:
Increased Load Times
Large JavaScript files can significantly increase the time it takes for a webpage to load. This can negatively impact user experience, especially for users with slower internet connections or those accessing the site on mobile devices.
Higher Bandwidth Consumption
Oversized files require more data to be transferred from the server to the client. This can lead to higher bandwidth costs and can be particularly problematic for users with limited data plans.
Impact on SEO
Slow-loading pages can lead to higher bounce rates, as users may leave the site if it takes too long to load. This can ultimately affect user satisfaction and engagement.
Impact on SEO
Search engines consider page load times as a ranking factor. Therefore, oversized JavaScript files can indirectly affect the site’s search engine optimization (SEO) and reduce its visibility in search engine results.
Rendering Blockage
Large JavaScript files can block the rendering of the page until they are fully loaded and executed. This can delay the display of the content and affect the perceived performance of the site.
How to Check the Issue
The Sitechecker SEO tool’s “Page Speed” category highlights specific performance issues that could slow down your website, one of which is “JavaScript file size is over 25 KB.” This particular issue is detected when a JavaScript file exceeds 25 KB, which can impact page load times and user experience.
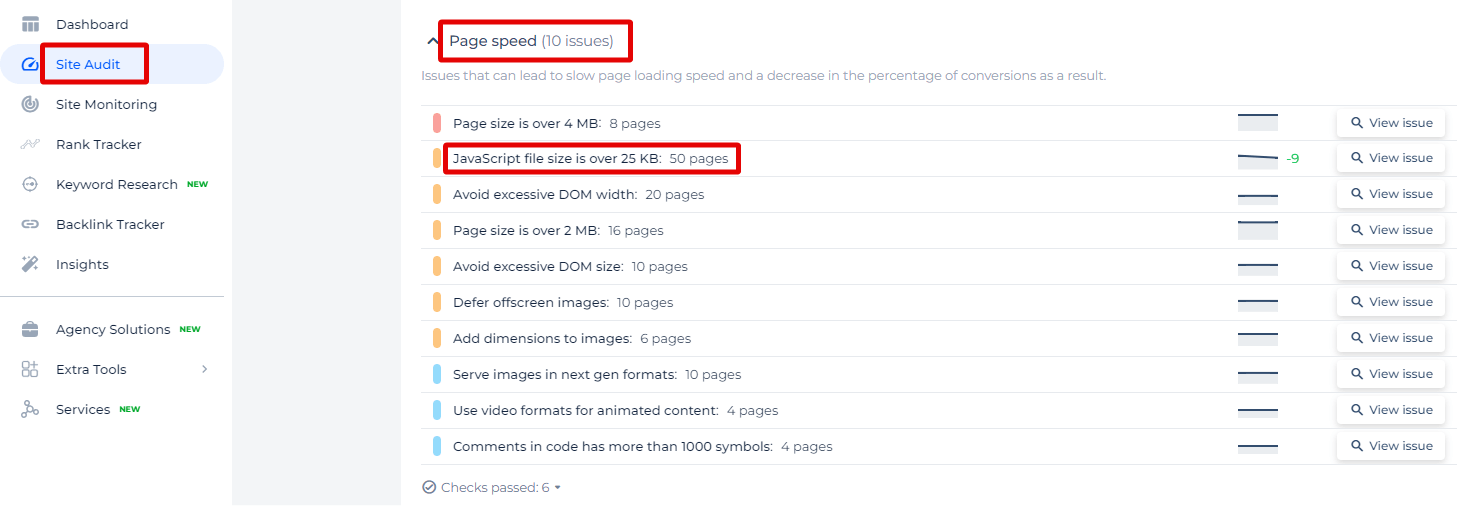
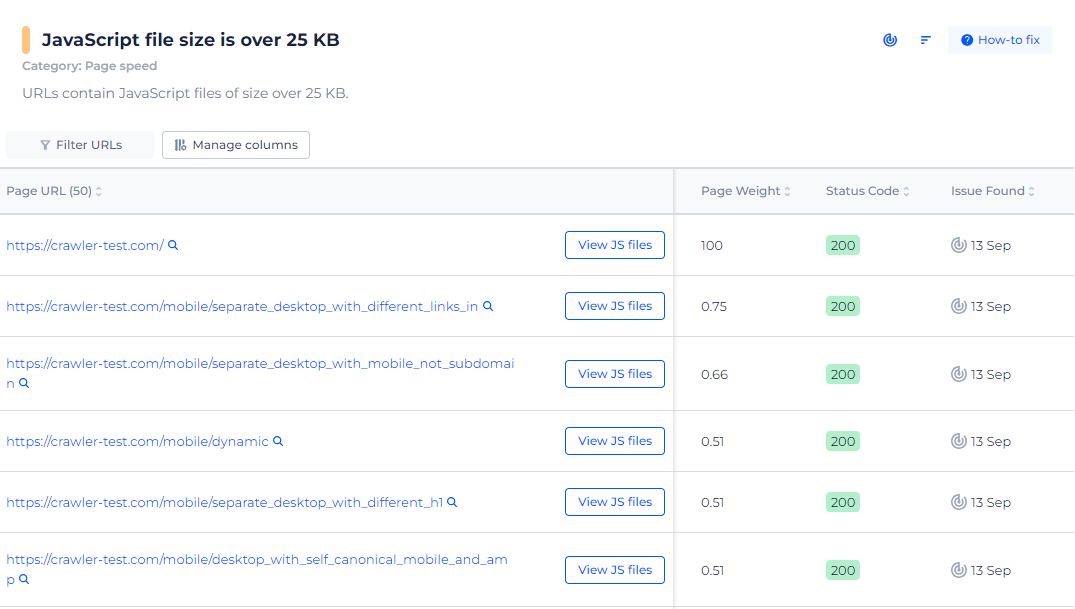
When you navigate to this issue within the tool, you’re not just presented with a number. Instead, the tool offers a comprehensive breakdown, including a list of pages affected by oversized JavaScript files. Each entry provides details like the file size and the specific JavaScript file causing the bloat, helping you pinpoint where optimizations are needed most.
Accelerate with JS Compression
Reduce your JavaScript file sizes and improve page load times with our easy-to-use Minify JS tool.
How to Fix the Problem
Fixing the issue of oversized JavaScript files involves several steps and techniques aimed at reducing the file size and optimizing their delivery. Here are detailed steps to address this problem:
1. Minification and Compression
Use tools like UglifyJS, Terser, or Google Closure Compiler to minify your JavaScript files. Minification removes unnecessary characters (like whitespace and comments) from the code.
npx terser yourfile.js -o yourfile.min.js
Enable Gzip or Brotli compression on your server. This reduces the file size when it’s transferred over the network.
Apache (Gzip)
<IfModule mod_deflate.c>
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/javascript
</IfModule>
NGINX (Brotli)
brotli on;
brotli_types application/javascript;
2. Code Splitting
Split your JavaScript into smaller chunks that can be loaded on demand using dynamic imports. This is commonly supported by modern bundlers like Webpack.
import(/* webpackChunkName: "myChunkName" */ './module')
.then(module => {
// Use the module
})
.catch(err => {
// Handle the error
});
3. Lazy Loading
Defer loading of JavaScript files that are not critical for the initial page load. This can be done using the async or defer attributes in your script tags.
<script src="non-critical.js" async></script>
<script src="critical.js" defer></script>
4. Tree Shaking
Use tree shaking to eliminate unused code. This is particularly effective when using ES6 modules with bundlers like Webpack or Rollup.
// Webpack configuration
module.exports = {
mode: 'production',
optimization: {
usedExports: true,
},
};
5. Optimize Dependencies
Audit your dependencies to ensure you’re only including what you need. Use tools like Bundlephobia to analyze the size of npm packages.
npx bundle-phobia --help
Replace large libraries with lighter alternatives if possible.
Example: Replace moment.js with date-fns or day.js.
6. Asynchronous Loading
Load JavaScript files asynchronously to prevent them from blocking the rendering of the page.
<script src="script.js" async></script>
<script src="script.js" defer></script>
7. Bundling and Module Concatenation
Bundle your JavaScript files to reduce the number of HTTP requests. Use tools like Webpack, Parcel, or Rollup.
npx webpack --config webpack.config.js
Enable scope hoisting to concatenate the scope of all your modules into a single scope, which can lead to smaller bundles.
module.exports = {
optimization: {
concatenateModules: true,
},
};
8. Monitor and Analyze
Use tools like Webpack Bundle Analyzer or Source Map Explorer to visualize the size of your JavaScript bundles and identify large dependencies.
npx webpack-bundle-analyzer dist/stats.json
9. Server-side Rendering (SSR)
If applicable, consider server-side rendering to reduce the initial load time by generating the HTML on the server and sending a fully rendered page to the client.
Using frameworks like Next.js for React applications.
10. Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Use a CDN to serve your JavaScript files. CDNs cache the files in multiple locations around the world, reducing the distance data has to travel and improving load times.
By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the size of your JavaScript files and improve your website’s performance and user experience.